Trap Mode¶
1. DEFINITION (What is it?)¶
This use case and the Snmptrap scenario enables you to gain real-time inventory of all connected assets ** on the network. All coomunication with the network assets takes places regardless of of the access layer and how the asset connected. Visibility and categorization of corporate and non-corporate assets (guests and BYOD) provides critical information for business and technical processes. All these assets **are discovered in passive and active modes, enabling non-intrusive deep asset knowledge. With this deployment you can identify WHEN and WHERE the asset is connected in real-time and have a historical view, asset TYPE (Laptop, printer, voIP phone, tablet, mobile phone, IOT, SmartTVs etc.) and additional information about its characteristics. All of this assets information is stored in a CMDB called openNAC CMDB, which stores assets characteristics and attributes in a flexible schema that can be easily expanded. This can be expanded manually by administrator to include business logic, map with internal processes etc. All the events that are harvested from openNAC technologies include information about all the asset’s context:
- Where the asset is connected from, the physical interface used.
- What type of device, laptop, printer, phone, security camera,IOT device of any connected asset.
- Technical information about the connected asset in the corporate network such as IP, MAC, services running, operating system etc.
- When it was connected, real-time and having audit tracing to establish a network access lifecycle.
This CMDB and its assets can be integrated and synced with other CMDB instances and asset repositories.
2. MECHANISMS (How does it work?)¶
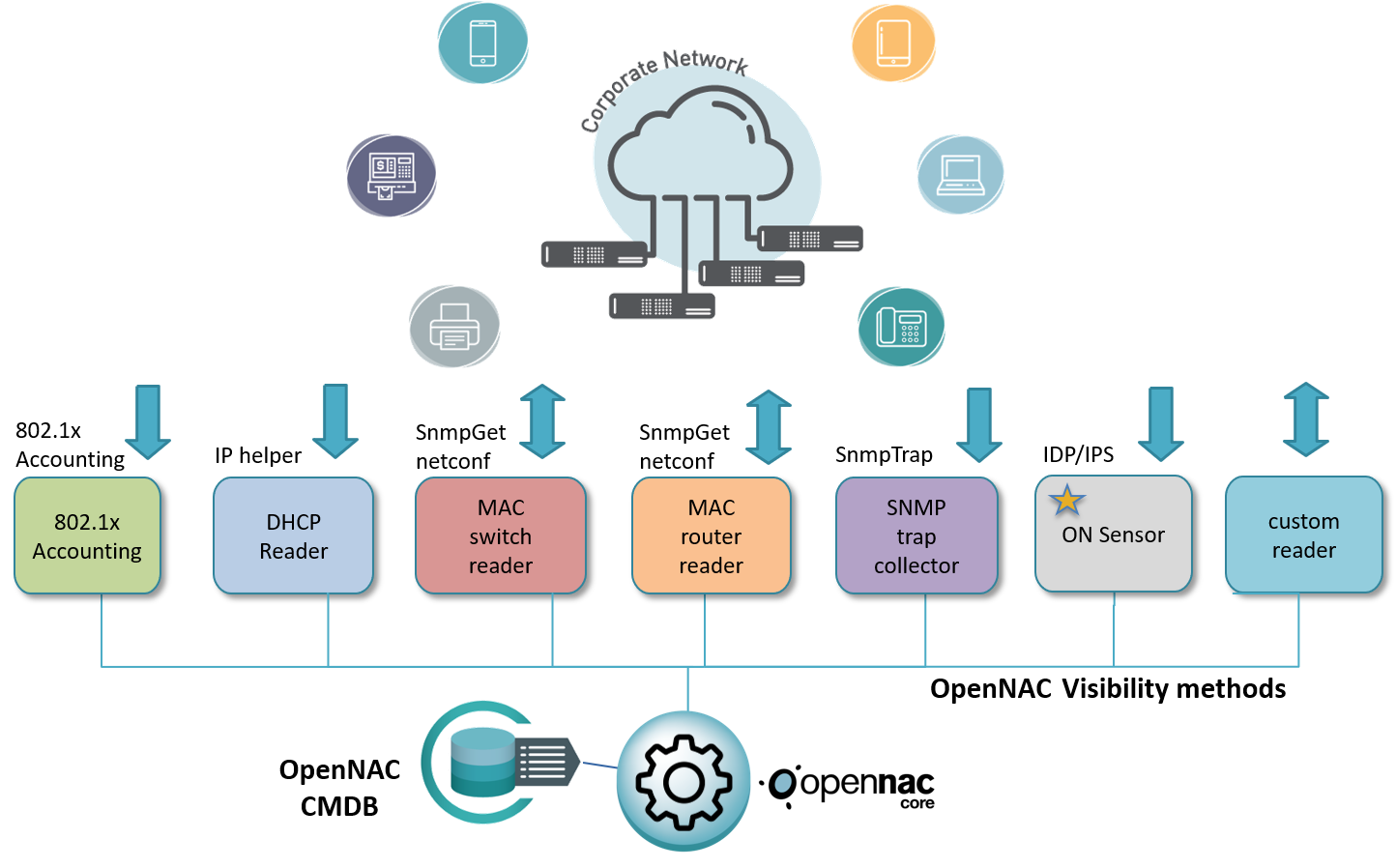
openNAC technologies support many different methods to gather information from corporative networks with the goal of being flexible, non-intrusive and user-friendly by using standard protocols that simplify deployment.
Visibility trap mode scenario can use the following methods to collect information from the corporate network to build the CMDB database automatically.
- 802.1x accounting events: Depending on the network capabilities it is possible to collect information from 802.1x accounting events gathered from users and devices connected to the corporate network, this is part of the AAA capabilities provided by network devices that support the 802.1x standard.
- DHCP requests events: openNAC harvests information from DHCP requests, reading and consuming the information provides useful asset data.
- MAC Table for switches and routers: For assets where static IPs are used this method can be a useful method to identify IP information and its MAC address, this method connects to network assets to extract MAC tables and stores the information in the openNAC CMDB.
- SNMP Traps events: “snmp-traps mac learn” disovers when and where a device is connected identifying its physical address commonly named MAC address.
- Custom reader: openNAC provide capabilities to expand visibility methods anabling it to create custom readers to the qualify partner.
Note
The openNAC sensor is only required to be used in visibility sensor mode deployment, this is an independent role that needs to be deployed in case of requiring visibility sensor mode deployment. It adds additional information to the SNMP Trap MODE
One of the main openNAC capabilities strenghts are the profiling methods, the system includes out of the box rules that enables discovery and classification off all assets connected to the network:
PROFILING METHODS:
- DHCP fingerprint: Extracts a lot information about the asset based on DHCP events, ip address, mac address, name of device, type of device based on dhcp class field and many others.
- AD Queries: Using AD queries to identify if the asset discovered is being managed by the active directory and identify if it is a corporative asset.
- OpenPorts: Discovers which ports are open on the asset in question.
- WMI: Enables us to use to launch commands and tasks with Windows assets to gain deeper discovery and profiling without any agent installation. WMI credentials must have specific privileges to carry out its queries and processes.
- SSH: Enables us to use ssh credentials to connect to network assets to launch commands and tasks to gain deeper discovery and profiling without any agent installation.
- BANNER: Enables us to get information from service banners to identify device use and typology.
- HTTP: Enables us to launch HTTP queries to identify banners and get information in order to identify exactly the assets connected to the network.
- ON Sensor: This visibility and profiling mechanism is not used in trap mode deployment but is based on the sensor mode deployment. This method allow us to gain visibility of your network through a passive service that inspects, in-depth, all traffic and shows all network activity, it includes http(s) sessions (web traffic) with the requested URL, DNS request and replies (Internal and external requests), SMTP sessions (e-mail traffic) and much more; based on this collected information you can configure different kind of policies to improve your network security.
- CDP - LLDP: This method collects layer 2 information, openNAC technologies connect to network devices and collect the information gathered through LLDP (The Link Layer Discovery Protocol) and CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol).
- SNMP: Gets information through snmp queries to network devices.
- Agent: openNAC agent allow us to get information about endpoints, security status, software inventory, hardware inventory and enables enforcement (launch commands). openNAC agent support major operating systems such as Windows, Linux (deb, rpm packages) and MAC OS.
- Portal: The user portal is one of the main pieces to deploy guest and BYOD use cases, the user portal can collect information such as IP, user agent and many others.
- SDK: openNAC can expand its profiling capabilities to cover additional customers requirements.
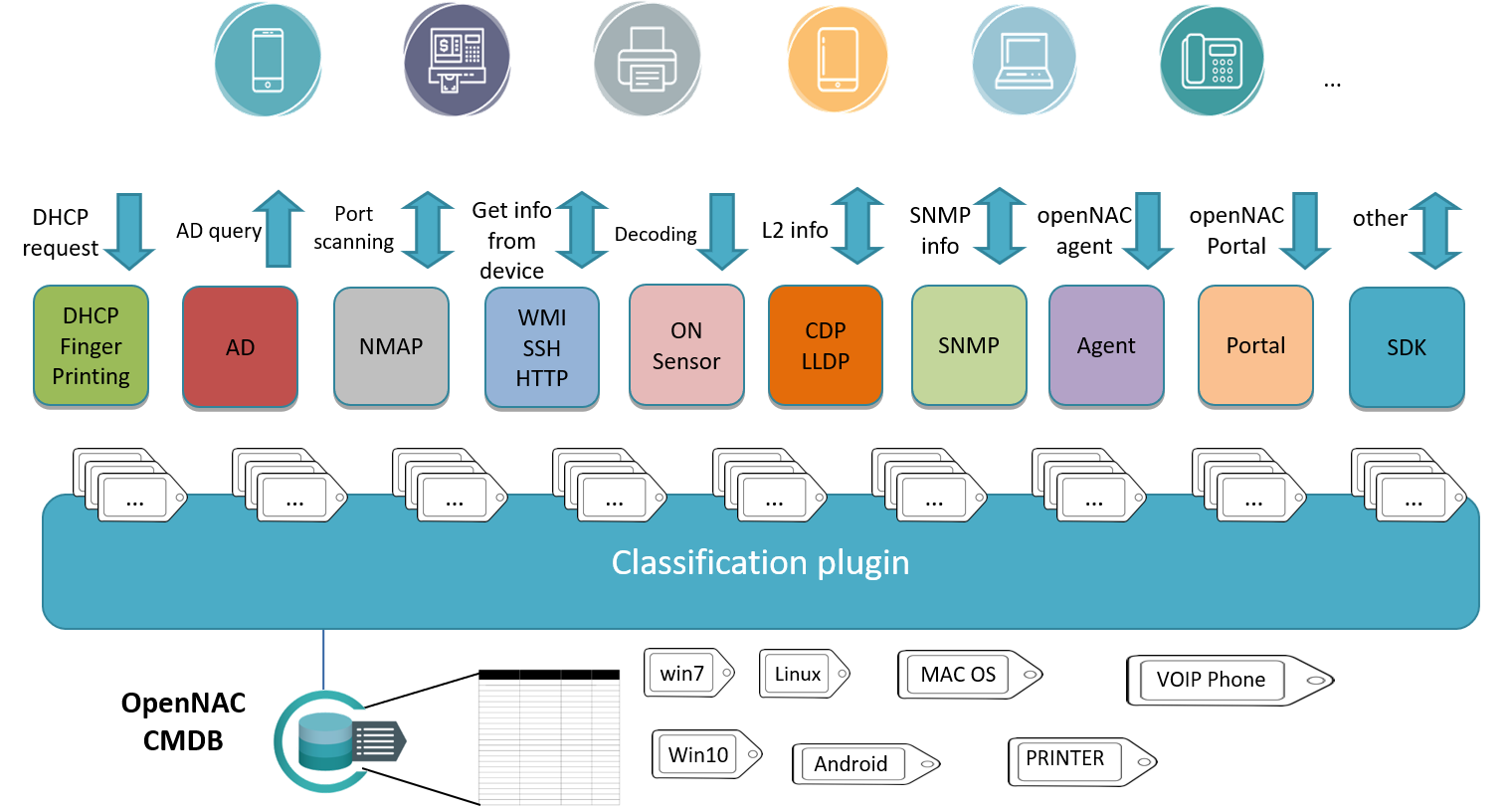
By default openNAC technologies include the capabilities to detect the type of devices connected in the network based on different tools and proccess, this is called asset profiling. There are two methodes for profiling:
- Automatic profiling where the system includes out of the box profiling rules that are updated frequently.
- Manual profiling this is where the administrator can define profiling rules manually with a few clicks and in a very intuitive way. Profiling rules can be expanded in order to identify the assets connected to the network and the following components can be used, DHCP Fingerprint, Ports, Banner, Snmp Service Information HTTP, MAC vendor, OS.
3. COLLECTED INFORMATION (What do we get?)¶
As soon as the visibility module is deployed the following information is gathered about the connected network assets:
- TIME: When was the last time the asset connected.
- IP ADDRESS: IP address assigned to the connected asset.
- MAC ADDRESS: Physical asset address.
- NAME OF THE DEVICE: Device name can be gathered by DHCP information, openNAC Sensor or others.
- NETWORK DEVICE IP ADDRESS: IP address of the network devices (switch, AP, VPN) where the asset is connected.
- NETWORK DEVICE MAC ADDRESS: MAC address of the network devices (switch, AP,VPN) where the asset is connected on the network.
- PHYSICAL PORTS: Interface where the asset was connected and discovered.
- TYPE OF DEVICE: Through profiling rules and its discovering mechanisms openNAC can identify the asset type.
- MAC VENDOR: Get the vendor assigned to the physical address (Mac address).
- OPENPORTS and BANNERS: The assets open ports and banners are identified enabling deeper understanding of its characteristics.
- TAGS: With plugins such as Discovey and profiling rules it is possible to identify open ports in asset and its type, openNAC uses TAGS to manage all of this information in a flexible way, the TAGs are stroed in the CMDB.
- The Tag=”DOP_TCP_9100” means that the asset has the port 9100 TCP open. The Tag=”EPT_PRINTER” means that openNAC has discovered a printer through its profiling rules.
4. DASHBOARD (How do we display what we know?)¶
The information can be visualized in different ways and formats.
- Business profiles: Allows us to group different policies then identify the assets that match with these network access rules. This is generally high level information that is leveraged for and by upper management. It can also be used to give a high-level progress status of a given situation; Nº of compliant / non-compliant devices, Nº of devices affected by Wannacry and presently in quarentine etc.
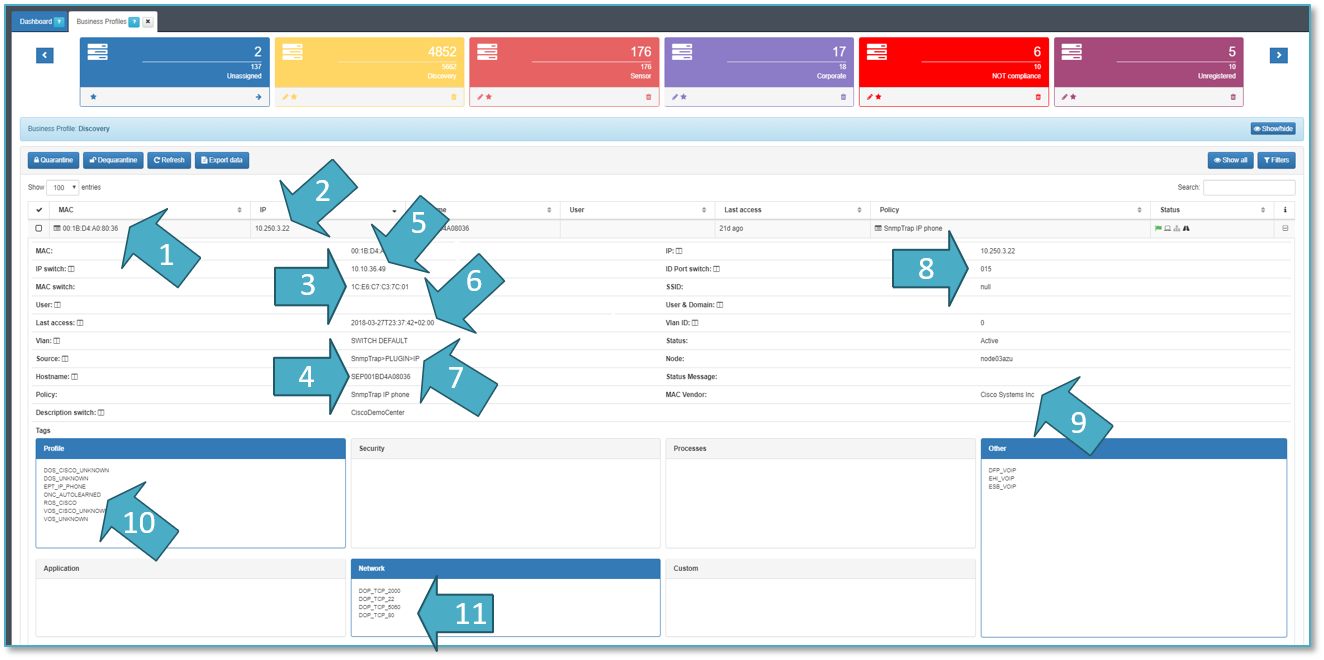
- USERDEVICE MAC ADDRESSES: 00:1B:D4:A0:80:36
- USER DEVICE IP ADDRESSES: 10.250.3.22
- NETWORK DEVICE MAC ADDRESS: 1C:E6:C7:C3:7C:01
- DEVICE NAME:SEP001BD4A08036
- NETWORK DEVICE IP ADDRESS: 10.10.36.49
- TIME: 2018-03-27T23:37:42
- SOURCE OF INFORMATION: SnmpTrap -> PLUGIN -> IP
- PHYSICAL PORTS: interface 0/15
- MAC VENDOR: Cisco Systems Inc.
- TYPE OF DEVICE: EPT_IP_IPHONE.
- OPENPORTS and BANNERS: DOP_TCP_5060
TAGS: open ports, device profile and others such as ROS_CISCO, ESB_VOIP.
- CMDB View: openNAC includes an internal CMDB that stores all asset information and its configuration, you can apply filters and serach by tags as shown bellow:
The tag EPT means End Point Type.
- Free search Analytics Engine
Opennac technologies includes the openNAC Analytics that provides a powerful search engine, allowing you to apply filters, time ranges and many others variable in a very intuitive way.
- Dasboard Analytics Engine
openNAC Analytics provides out of the box dashboards that allow you to visualize historic and new data information in realtime.
5. DEPLOYMENT (Do it yourself)¶
5.1 REQUIREMENTS FOR TRAP MODE:¶
- openNAC Core is deployed on the network.
- Network devices(switch, ap..) with snmp-traps mac learn.
- openNAC Analytics.
- Client PC, in the following scenario we will use Windows but any asset can be used.
- DCHP information, is collected by openNAC using the service dhcp-reader.
This use case is based on snmp traps and plug-ins
We are going to use two plugins for this use case and scenario:
- Discovery plugin is required.
- Dnshostchecker plugin is required.
- Profiling rules.
5.2 SCENARIO ARCHITECTURE¶
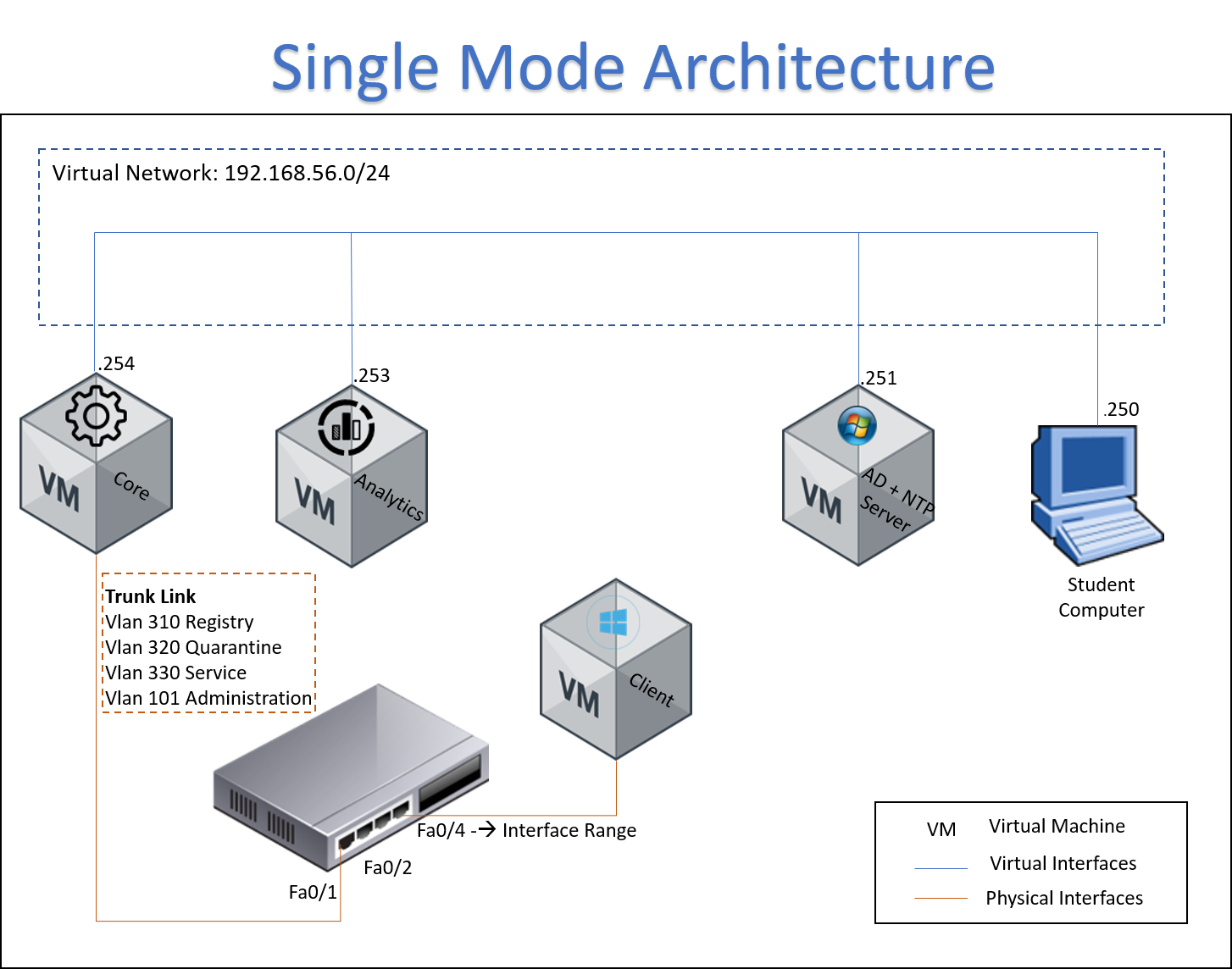
The following image shows the flow for SnmpTrap Mode, it can be used to calrify how it works, and it is a useful from a troubleshooting point of view.
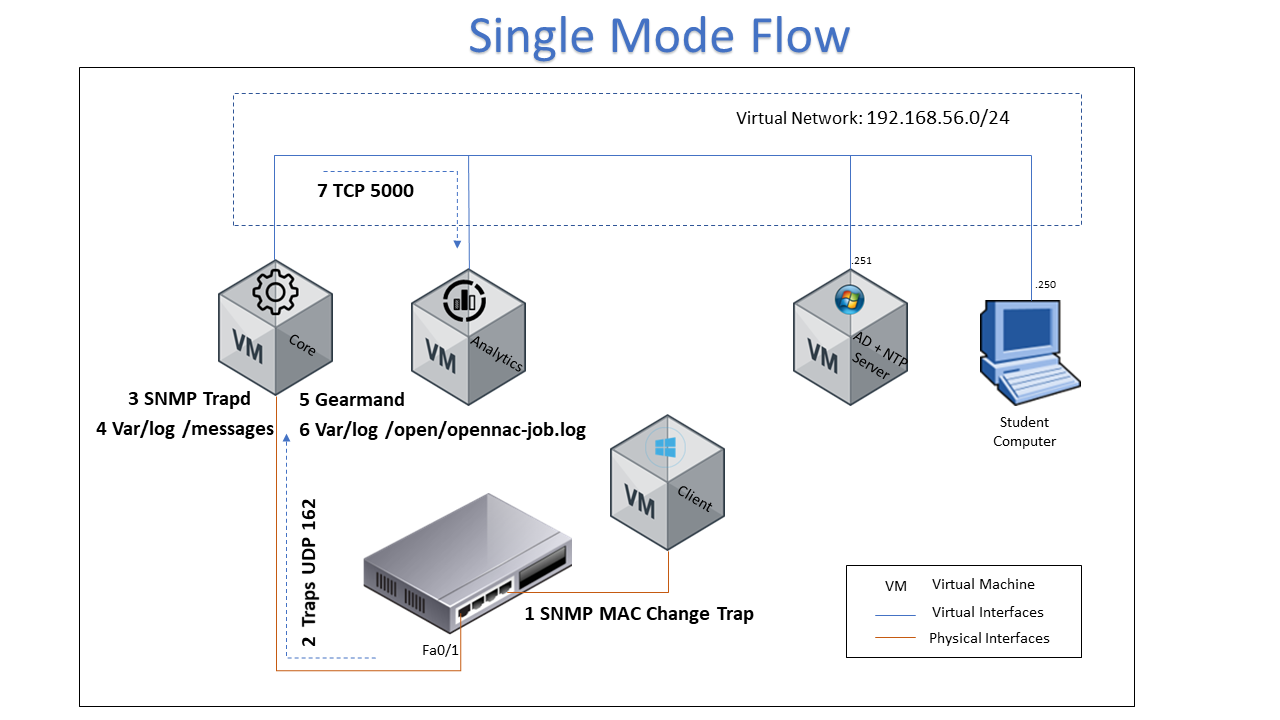
- The SNMP trap is generated by a network device, traps are generated by a MAC change on a specific port.
- The SNMP trap is sent to ON Core using UDP protocol and port 162
- The ON Core device should have the snmpd daemon listen for the switch trap
- A message is saved on var/log/messages directory, this message is about SNMP trap information
- Gearmand service should be enabled to manage the SNMP information between location and the ON Core device
- The file var/log/opennac-job.log contains the entire SNMP trap information
- The information about the devices connected to network will be sent to Analytics for processing using TCP protocol port 5000
5.3 SETTINGS FOR TRAP MODE:¶
ON Core
Start and configure openNAC Core.
openNAC Core Deployment Guide.
Open the web console, go to Configuration on the left hand side bar menu, Select the option Configuration vars, then select Plugins tab, enable Discover and OpenPorts Plugings and save.
For more information visit the :ref:openport plugin section`<pluginopennports>`.
Go to ON NAC in the bar menu, click on Policy and select Add new option to create the policy for SnmpTrap mode scenario.
In General tab set the policy name, check Yes option for enable the policy and add comments if you require.
In preconditions: Sources tab, enable the option SNMP Trap
In postconditions tab, select Set VLAN option and check VLan 0 and confirm.
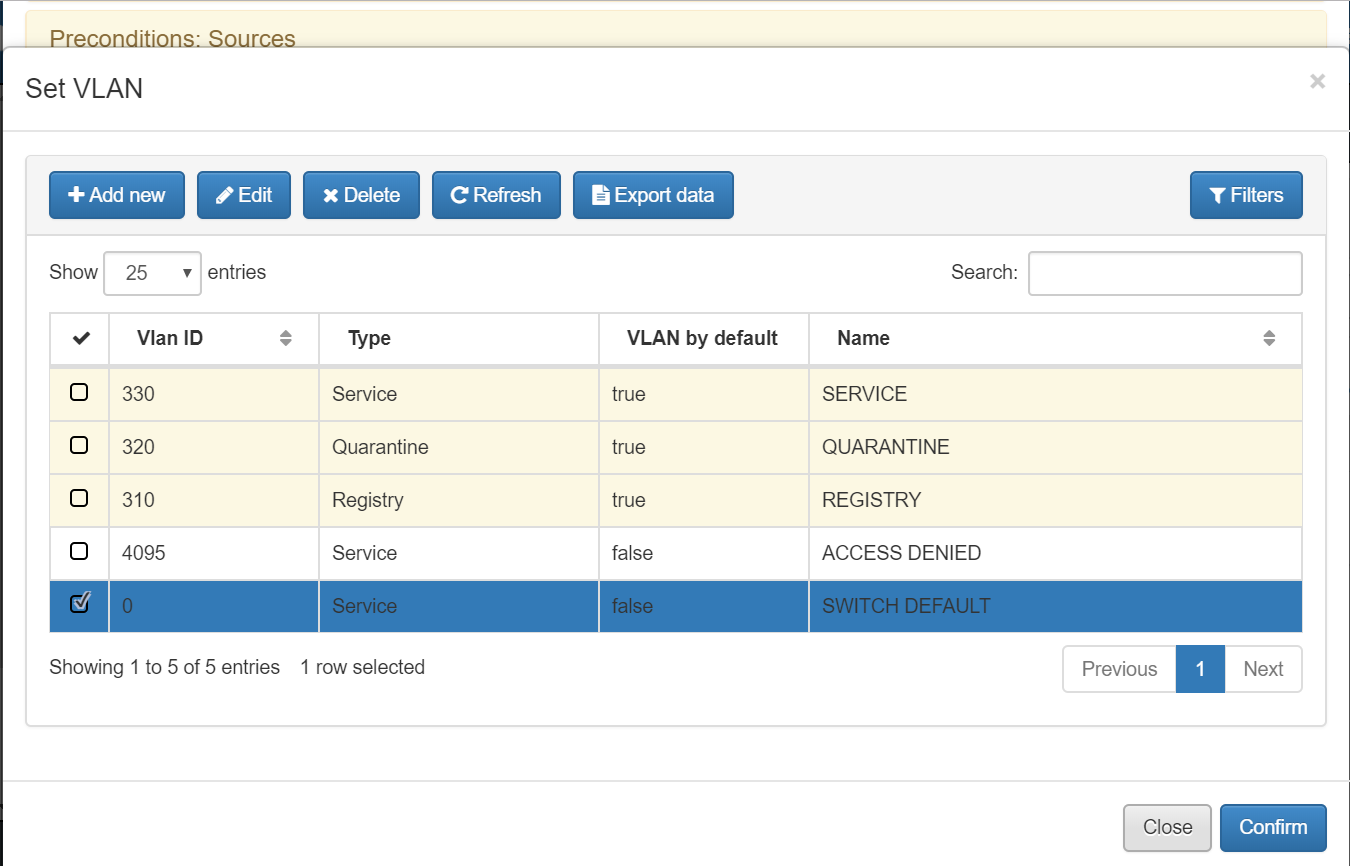
In postconditions tab, go to Plugings and enable the Discover and OpenPorts for this policy.
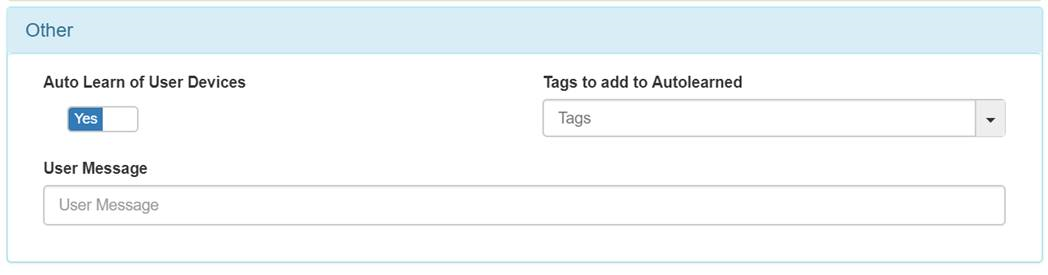
In other tab enable the Auto Learn of User Devices option.
ON Analytics
Start and configure openNAC Analytics
openNAC Analytics Deployment Guide.
Switch
The first step to take on the switch is to configure the SNMP traps, so please review the following link to check the required configuration
Additionally be sure that the access ports has been assigned to service VLAN 30, and there’s a DHCP server working on.
DHCP Server
There’re three ways to set a DHCP server:
- IP Helper from (L3 Devices)
- DHCP Reader from the Sensor
- DHCP Reader from the OpenNac Core
In a Lab environment sometimes L3 devices are not available, so we are going to check the option 2 and 3.
1.DHCP Reader From L3 Device
In the productive environment a DHCP Server should always be available so, if the ON Core is in the same VLAN or it has access to read the DHCP traffic, only one thing is left to be done to obtain the information from this server; enable the service dhcp-helper-reader. Before, please be sure to get the DHCP information.
tcpdump -i eth0 port 67
service dhcp-helper-reader start
You can verify the collected information through the ON NAC web console –> Business Profiles
2. DHCP Server From Sensor
3. DHCP Server From Core
In initial configuration wizard you set the scope for service VLAN, the switch ports used for testing should be assigned to the service VLAN. The dhcpd service should be running on core device.
service dhcpd (start|stop|restart|status)
5.4 PROFILING:¶
As a first part of visibility use case implementation, OpenNac can separate the discovered devices according with its type, if is phone, desktop, printer, server, etc. This objective can be accomplished using the collected information and checking different parameters as O.S, DHCP fingerprint, ports, etc.
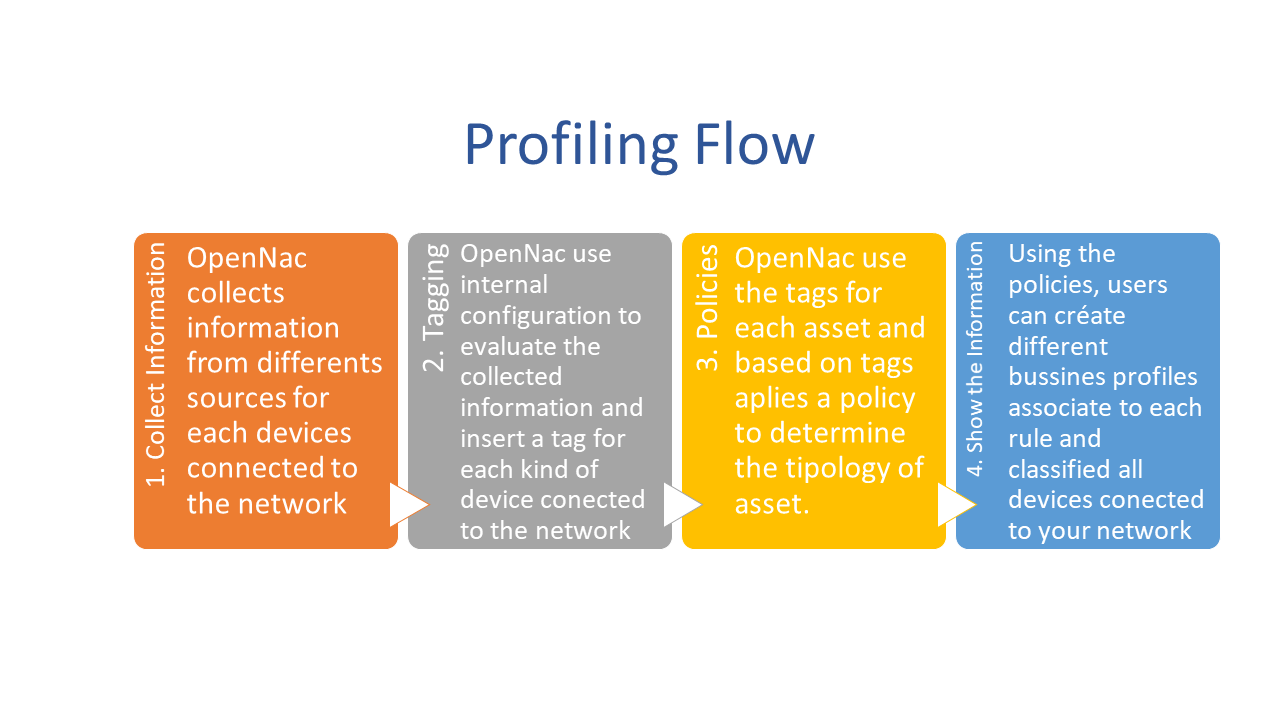
- The first step is collect the information using visibility use case configuration, it can be done using traps, sensor, DHCP traffic, etc. Visibility Methods
- The second step is tag the discover devices using different parameters. These parameters can be edited:
- Review: ON NAC –> Profiling –> User devices. OpenNac checks MAC vendor, used ports, DHCP fingerprint and based on these information classifies the devices.
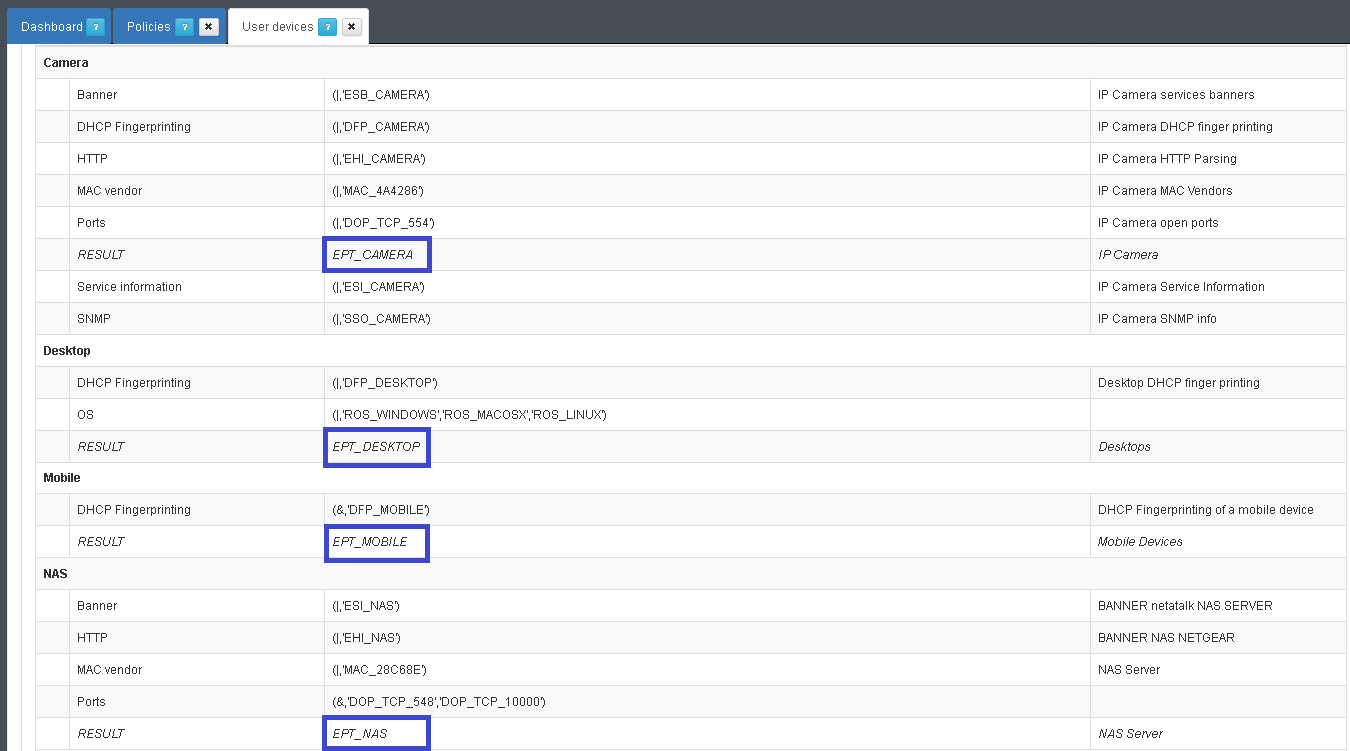
OpenNac core includes a pre-defined profiling rules for each devices, but according with the deployment the user can customized the evaluated parameters.
- The third step is set the policy based on tag, there’re several predefined tags but is possible to customize.
- Review: ON NAC –> Policies
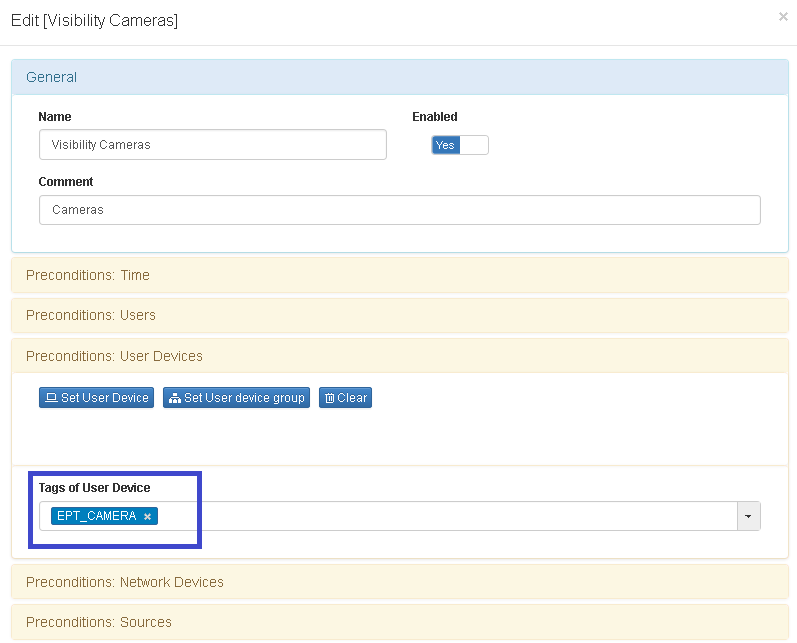
- The last step is associate the policy to business Profile
- Review: ON NAC –> Business Profiles
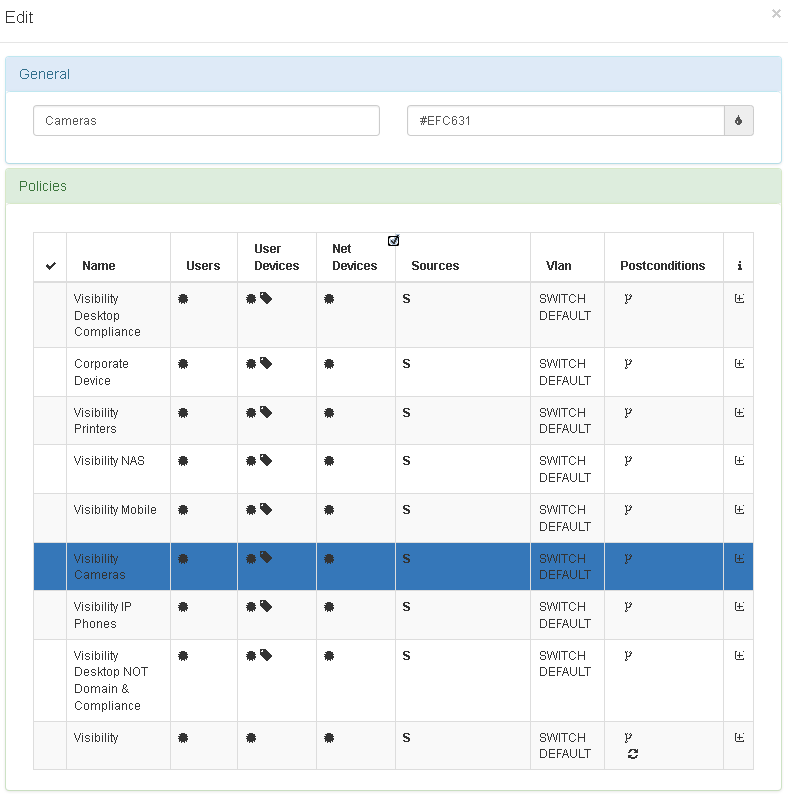
5.5 TESTING:¶
Connect a client to the switch interface. Verify the IP configuration of the host, the IP address of the service VLAN should be automatically assigned by the dhcp server. On the web administration console go to ON NAC -> Business Profiles and check the list, verify the mac address, the IP, and the information collected by plugins for each connected device
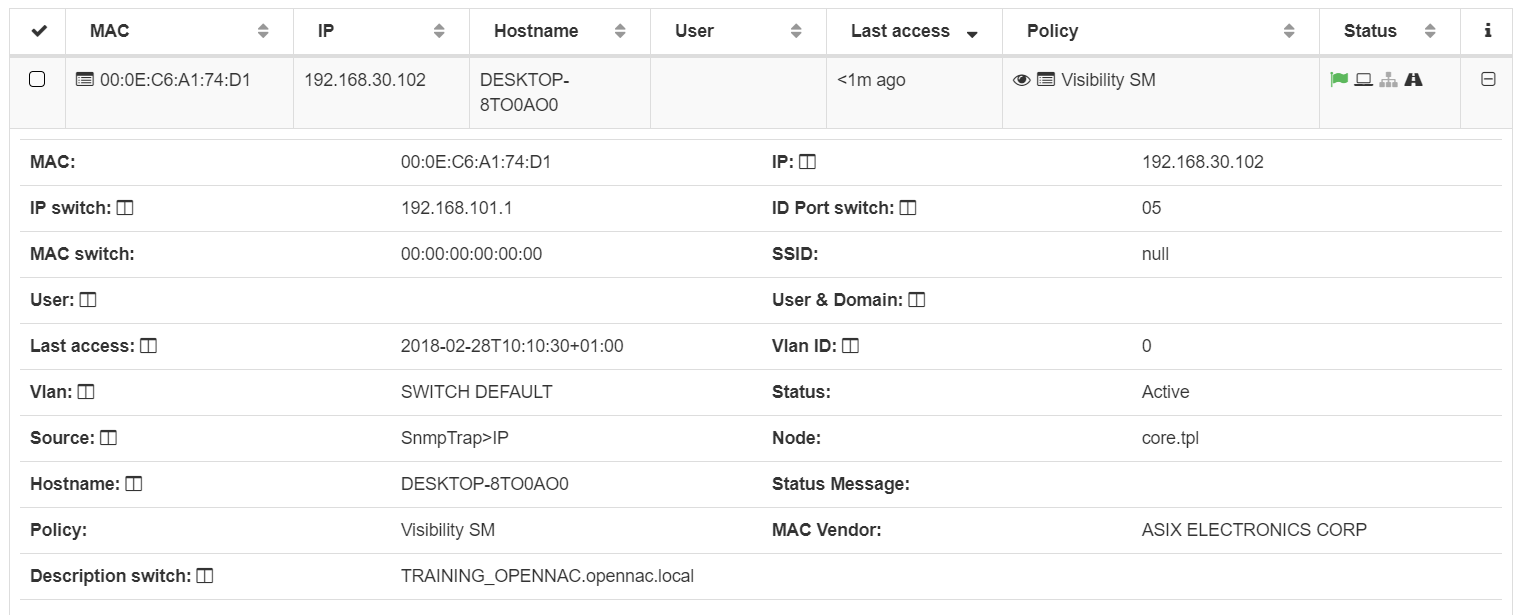
Go to Analytics -> Discover, select the opennac-* and verify the events related with MAC discover.
5.6 TROUBLESHOOTING FOR TRAP MODE:¶
Please perform a basic review Basic Check
You can verify the SNMP Flow SNMP Traps Troubleshooting