1.2.8. ARP
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a fundamental networking protocol used to map IP addresses to corresponding MAC addresses on a local area network (LAN). In a networked environment, devices communicate using IP addresses, but data is transmitted at the link layer using MAC addresses. ARP acts as the bridge between these layers by dynamically discovering the MAC address associated with a specific IP address.
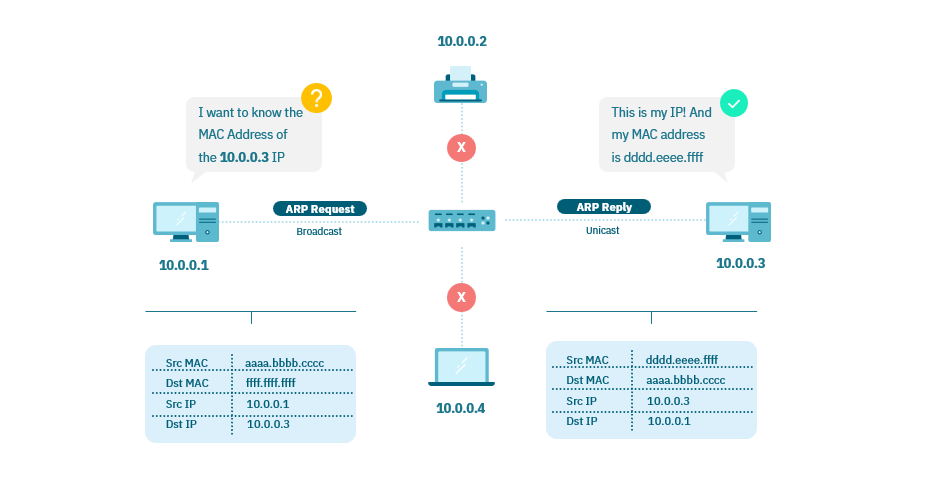
When a device needs to communicate with another device on the same network, it sends an ARP request to ask for the MAC address corresponding to a given IP address. The target device, if present on the local network, responds with an ARP reply, providing its MAC address. This information is crucial for efficient data transmission within the network, as it enables devices to build and maintain ARP tables, facilitating accurate and timely communication.