3.1.10.5. Wizards
3.1.10.5.1. Initial Configuration Wizard
As soon as ON Core is deployed a configuration Wizard is launched to simplify network access integration. With this Wizard the system will ask for common information such as switch parameters, VLANs, DHCP scopes, Captive portal information, etc.
This Configuration Wizard can be launched on demand to modify parameters affected by the wizard. To do that, go to Configuration > Wizards > Initial configuration Wizard, and to follow the wizardclick on the double arrow button.
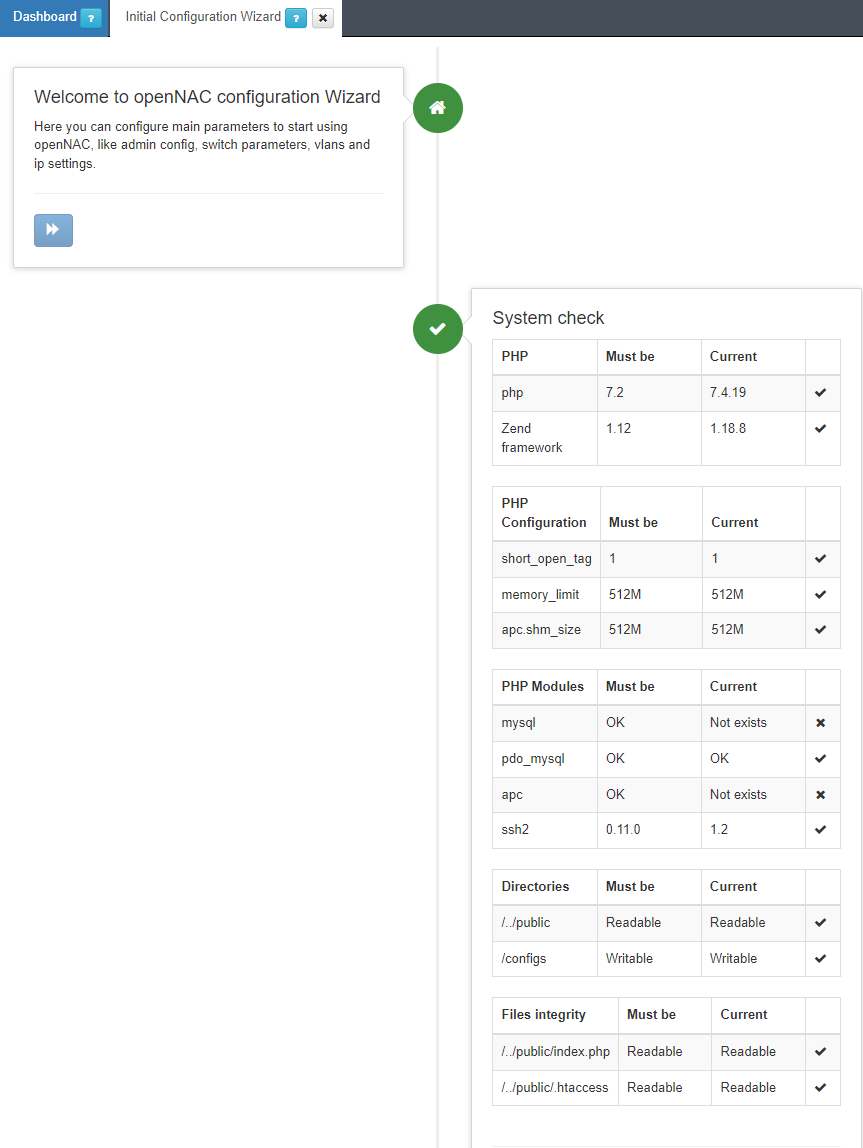
3.1.10.5.1.1. System Check
First, we will see the System check to verify various packets, directories, files, modules, and configurations.
3.1.10.5.1.2. Administrator info
Once we check the system, the Administrator info section will appear, and we will be able to enter the following parameters:
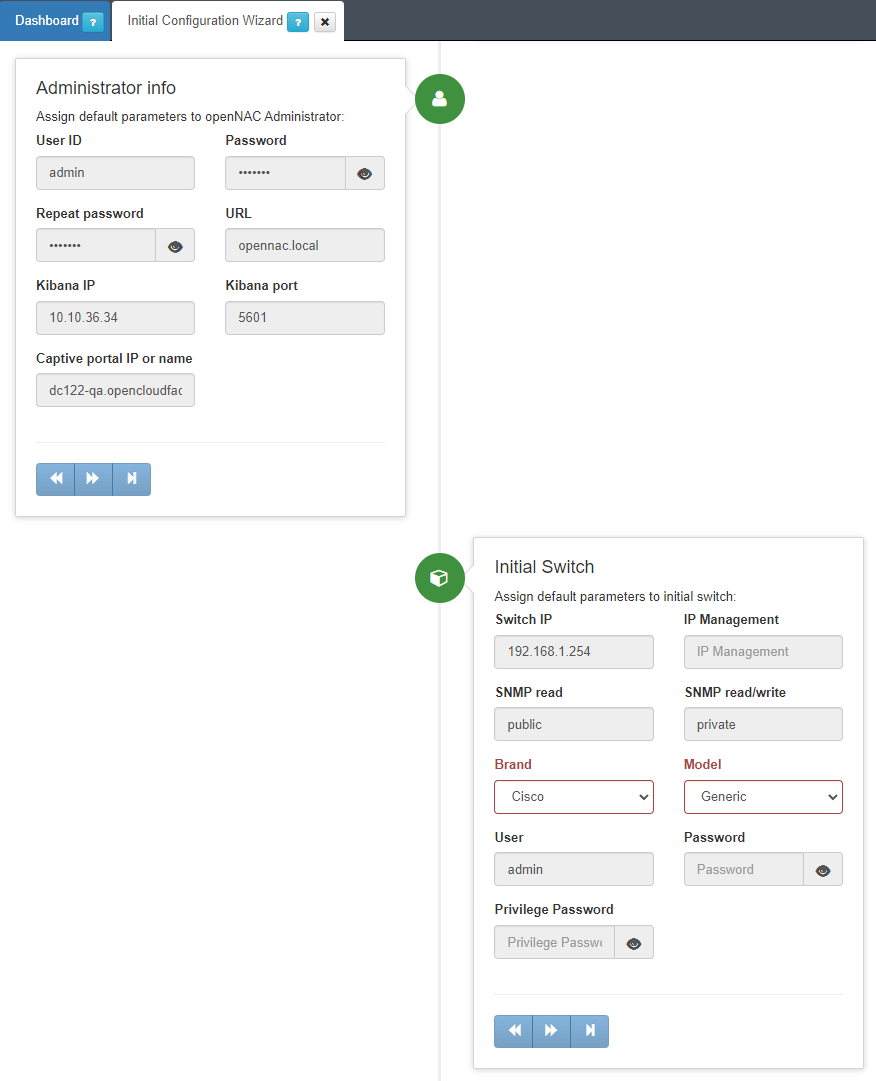
User ID: To change the default product User ID. Admin is the default one.
Password: To change the admin’s password.
Repeat password: To double-check the password.
URL: To change the URL assigned to the Web Administration portal. By default, the value is ON_VAR.local.
Kibana IP: To define the onanalytics IP where the Kibana is running.
Kibana port: To define the port where Kibana is running.
Captive portal IP or name: To change the IP assigned to the user portal or captive portal. You can also enter the domain name.
3.1.10.5.1.3. Initial switch
The second section called Initial switch allows you to integrate the first switch in the deployment, which is very useful for POCs. It includes the following fields that should be completed:
Switch IP: To add the switch IP. This IP is the IP used to connect to the switch from ON Core.
IP Management: To add the management IP when the management IP is different than the switch service IP.
SNMP read: To configure the SNMP read community to be used by OpenNAC Enterprise and integrate with the switch. For read-only tasks.
SNMP read/write: To configure the SNMP read/write community to be used by OpenNAC Enterprise and integrate with the switch. For read/write tasks.
Brand: To configure the Brand for the switch that is being integrated (for instance, Cisco, HP, and many others).
Model: To configure the model used in the integration (for instance, 2900, 3500)
User: To configure the username used by OpenNAC Enterprise to manage the switch.
Password: To configure the password used by OpenNAC Enterprise to manage without privileges the switch.
Privilege password: To configure the privilege password used by OpenNAC Enterprise to manage the switch.
3.1.10.5.1.4. Quarantine VLAN
The Quarantine VLAN section allows for the creation of Quarantine VLANs in the initial OpenNAC Enterprise deployment. If you want to send any user to the quarantine network, these changes must be made. OpenNAC Enterprise can be a DHCP server and DNS server for this network. In that way, this assistant allows configuring DHCP scopes and defining the DNS for the clients. The DNS is poisoned so all user’s traffic is forwarded to the captive portal to inform the user and re-evaluate the policy. It includes the following fields that should be completed:
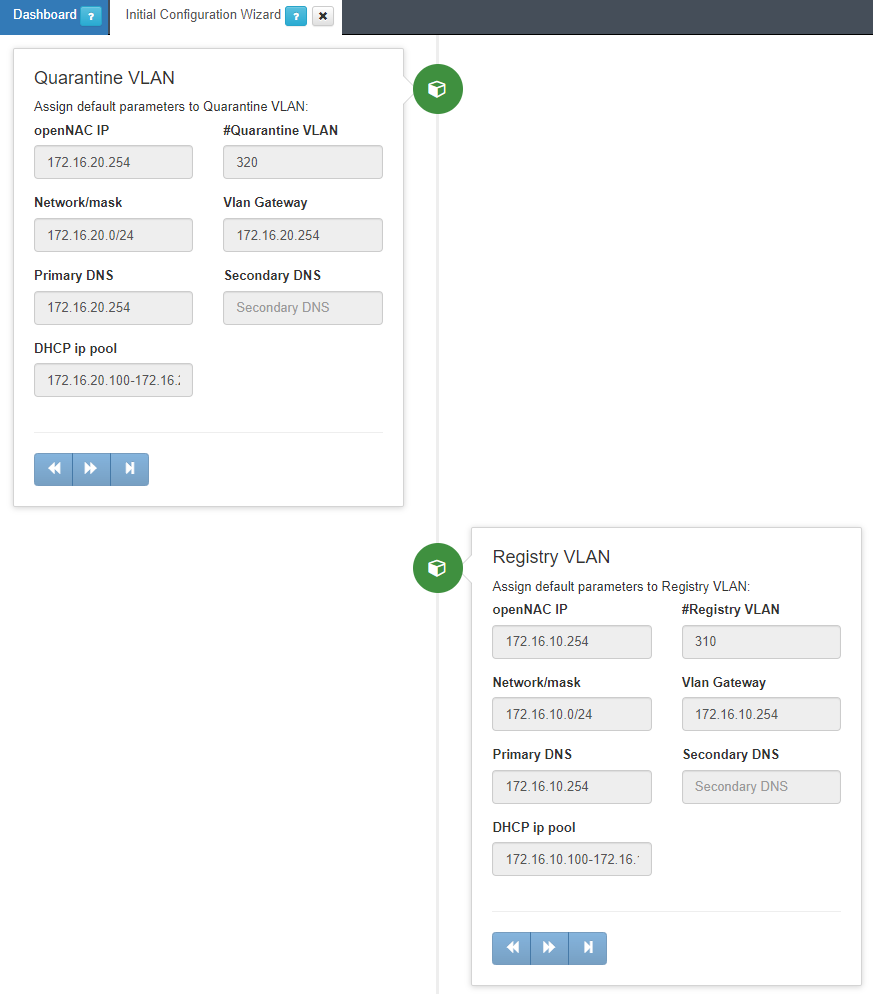
ON_VAR IP: To add the IP for the OpenNAC Enterprise server in the Quarantine network (this is only an inventory). If OpenNAC Enterprise requires this IP, this IP should be changed using SSH and through Linux commands and configuration files as explained in section Install and deploy ON Core. By including this IP, an exception will be created in the DHCP server to avoid IP assignment overlapping. This IP is used to access the ON Core IP in the Quarantine network. Normally these VLANs are routed and will be used as VLAN Service.
#Quarantine VLAN: To define the VLAN ID for the quarantine VLAN.
Network/mask: To define the DHCP Scope for this network.
VLAN gateway: To define the default gateway assigned by the DHCP to this network.
Primary DNS To configure the Primary DNS assigned to the clients. Keep in mind that in case OpenNAC Enterprise DNS is not used in the network, the DNS must be poisoned pointing to ON Core IPs.
Secondary DNS To configure the secondary DNS assigned to the clients through DHCP.
DHCP ip pool To define the name of the quarantine scope used by the configuration files.
ON Core can provide DNS and DHCP services in the network if required. This is not mandatory and commonly corporate DNS and DHCP services are used.
3.1.10.5.1.5. Registry VLAN
The Registry VLAN section allows for the creation of a Registry VLAN in the initial OpenNAC Enterprise deployment. If you want to send any user to the registry network, these changes must be made. The Registry VLAN can be used in Guest/Partner management networks, BYOD deployments, and others. OpenNAC Enterprise can be a DHCP server and DNS server for this network. In that way, this assistant configures DHCP scopes and defines the DNS for the clients. The DNS is poisoned so all user traffic is forwarded to the captive portal that allows Guest and BYOD management capabilities. It includes the following fields that should be completed:
OpenNAC IP: To add the IP for the ON_VAR server in the Registry network (this is only an inventory). In case ON_VAR requires this IP, this IP should be changed using SSH and through Linux commands and configuration files as explained in section Install and deploy ON Core. By including this IP, it will be created an exception in the DHCP server to avoid IP assignment overlapping. This IP is used to access the ON Core IP in the Registry network. Normally these VLANs are routed and will be used as VLAN Service.
#Registry VLAN: To define the VLAN ID for the Registry VLAN.
Network/mask: To define the DHCP Scope for this registry network.
VLAN Gateway: To define the default gateway assigned by the DHCP to this network.
Primary DNS: To configure the Primary DNS assigned to the clients. Remember that in case OpenNAC Enterprise DNS is not used in the network, the DNS must be poisoned pointing to ON Core IPs.
Secondary DNS: To configure the secondary DNS assigned to the clients through DHCP.
DHCP IP pool: To define the name of the registry scope used by the configuration files.
3.1.10.5.1.6. Service VLAN
The Service VLAN section allows for the creation of a Service VLAN in the initial OpenNAC Enterprise deployment. If you want to send any user to the service VLAN, this must be defined. Service VLAN is the common VLAN used by employees. This can be modified and expanded including other VLANs and proposes. Network segmentation is a common use case covered by the OpenNAC Enterprise solution. OpenNAC Enterprise can be a DHCP server and DNS server for this network. In that way, this assistant allows configuring DHCP scopes and defining the DNS for the clients. The DNS is poisoned so all user traffic is forwarded to the captive portal that allows Guest and BYOD management capabilities. This section includes the following fields that should be completed:
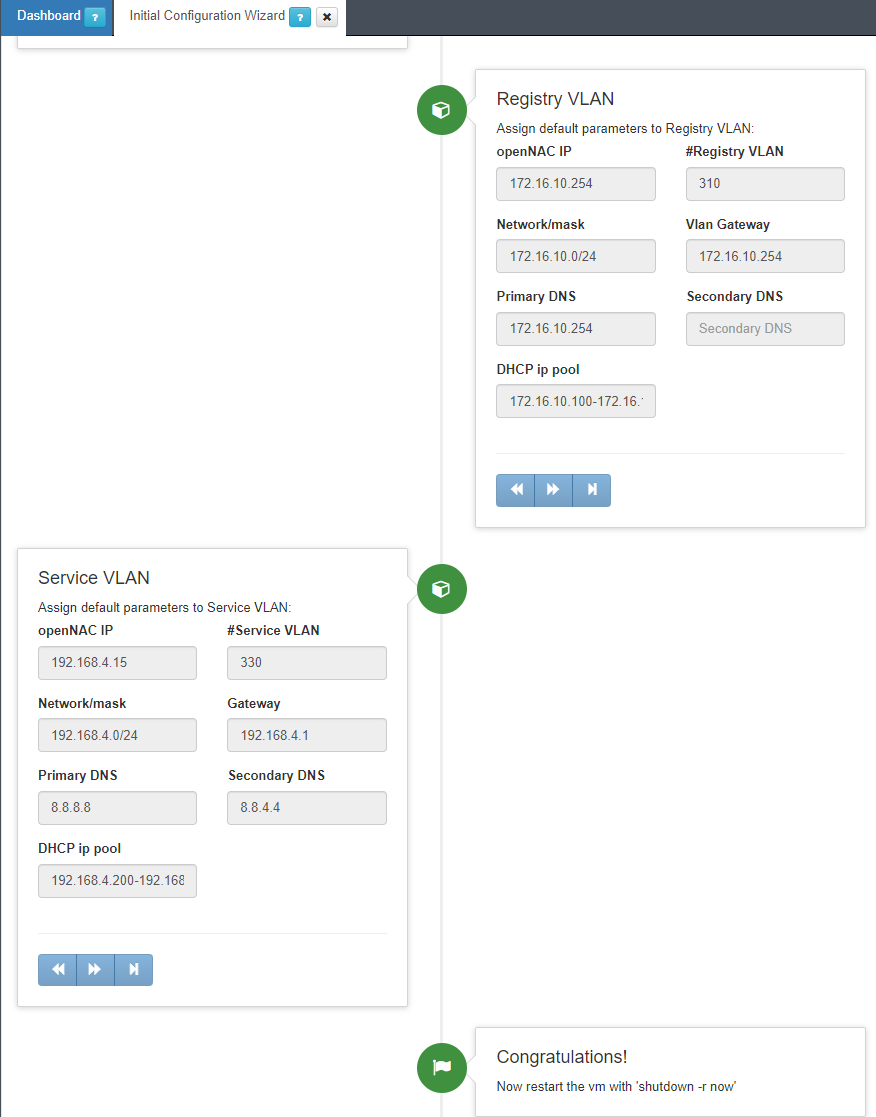
OpenNAC IP: To add the IP for the OpenNAC Enterprise server in the Service network (this is only an inventory). In case OpenNAC Enterprise requires this IP, this IP should be changed using SSH and through Linux commands and configuration files as explained in the section Install and deploy ON Core. Including this IP will create an exception in the DHCP server to avoid IP assignment overlapping. Normally the VLANs are routed and the VLAN Service IP will be used by quarantine and registry VLANs. This will publish captive portals (quarantine, ON_VAR agent, registry) to all the networks (Quarantine, registry)
#Service VLAN: To define the VLAN ID for the service VLAN.
Network/mask: To define the DHCP Scope for this service network.
Gateway: To define the default gateway assigned by the DHCP to this network.
Primary DNS: To configure the Primary DNS assigned to the clients through. Remember that in case OpenNAC Enterprise DNS is not used in the network, the DNS must be poisoned pointing to ON Core Ips.
Secondary DNS: To configure the secondary DNS assigned to the clients through DHCP.
DHCP ip pool: To define the name of the registry scope used by the configuration files.
As soon as the initial configuration is carried out the system should be restarted.
Note
If the OpenNAC Enterprise server is not acting as a DNS Server (Poisoned) or DHCP server for any VLAN, there is no need to restart the system.
3.1.10.5.2. Join Domain Wizard
One of the main wizards created in OpenNAC Enterprise is the one that enables joining the ON Core with an Active Directory domain.
Go to Configuration > Wizards > Join domain Wizard.
The Join domain Wizard tab displays the following fields:
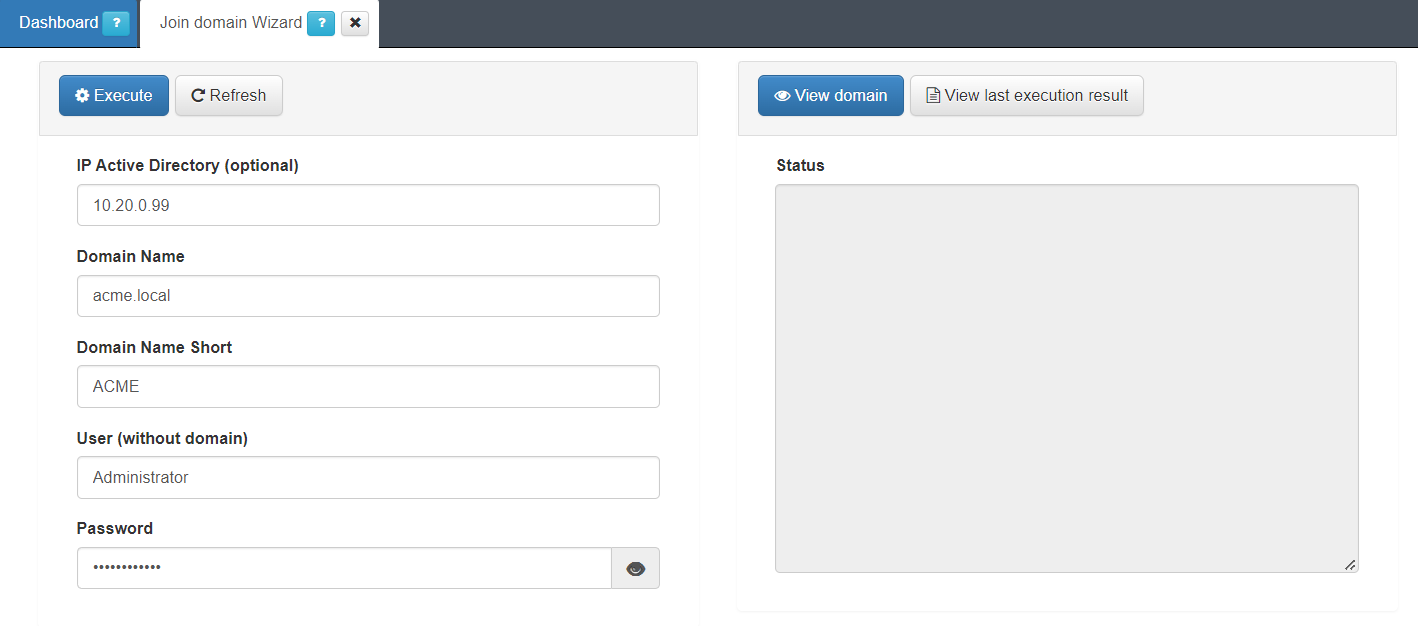
IP Active Directory: This is the Ips of the domain controller. This can include several IPs separate by a “,”.
Domain Name: This is the fdqn for the domain.
Domain Name Short: this is typically the netbios name for the domain.
User: This is the username that must have right to add workstations to the domain.
Password: this is the password for the user in the domain.
As soon as we have included the information, we can start the execution:
Click on Execute
A window will appear asking if you want to add a new UDS (User Data Source). Click on yes to add it.
A new window will appear with the information pre-filled based on the previously entered data. Modify the information if needed
Click on the Accept button.
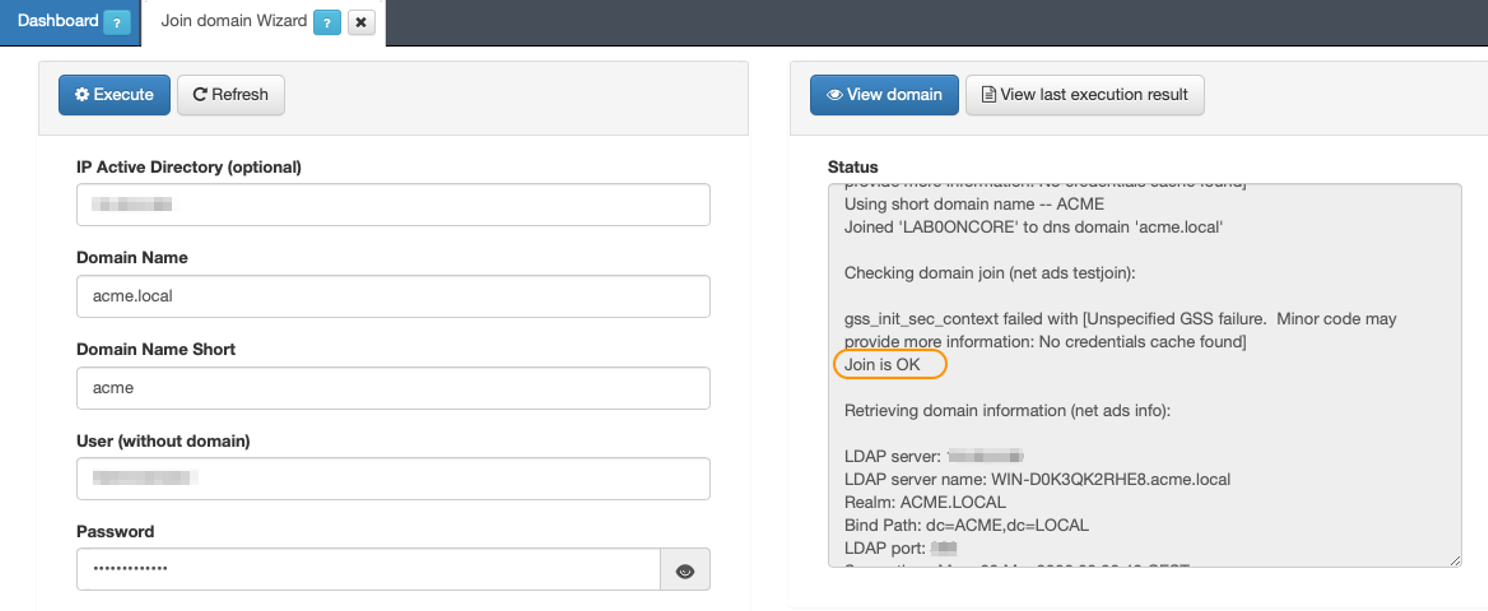
The right section of the window called “Status”, will display the progress of joining the domain. If an error occurs, it will be shown there. If everything goes well, you will see the string “Join is OK”.
Verify that the UDS is in the “ready” state.
Go to “ON CMDB > User Data Sources”
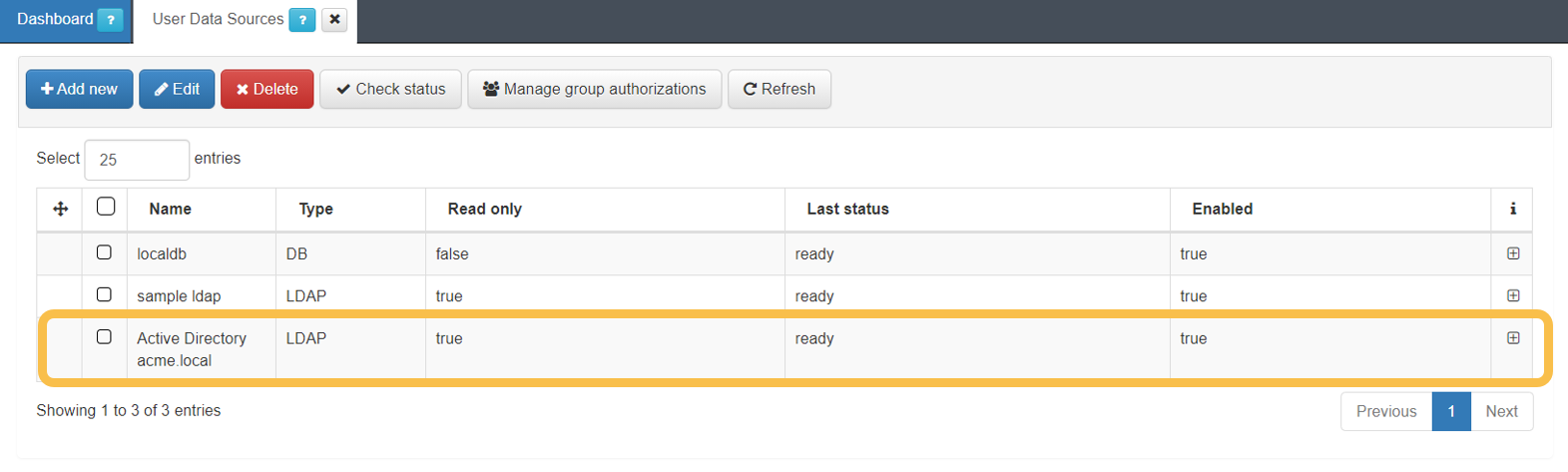
If the new UDS has the status “ready” there is nothing else to do.
- Otherwise:
Select it
Click on the Check status button.
If there are no errors, the UDS will change its status to “ready”.
3.1.10.5.2.1. Domain join issues
If you have any problems joining the ON Core with an Active Directory (AD) domain, verify the following steps to make sure that the union has been carried out correctly.
Note
The Active Directory integration only permits us to become a part of a domain. Configuring the NTP server on the ON Core server is also necessary.
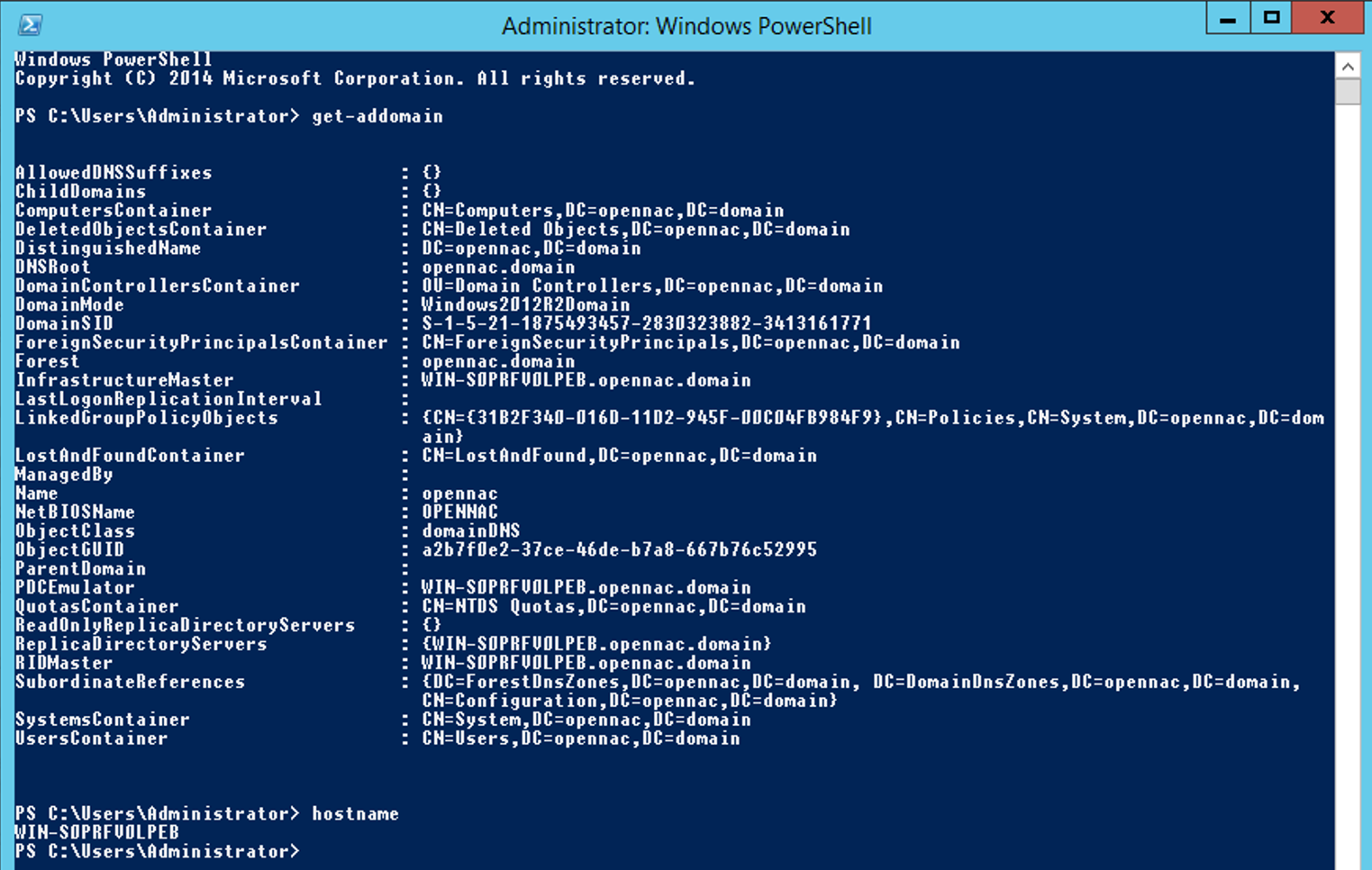
Before making any changes to the ON Core, verify the hostname of the AD server using the following CLI commands:
hostname
get-addomain
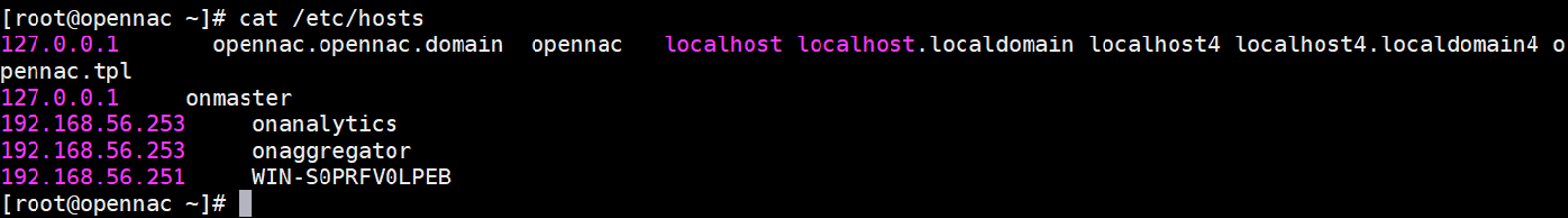
Add the hostname of the AD server to the host file in the etc directory. You can also use a DNS server to resolve the AD Server name.
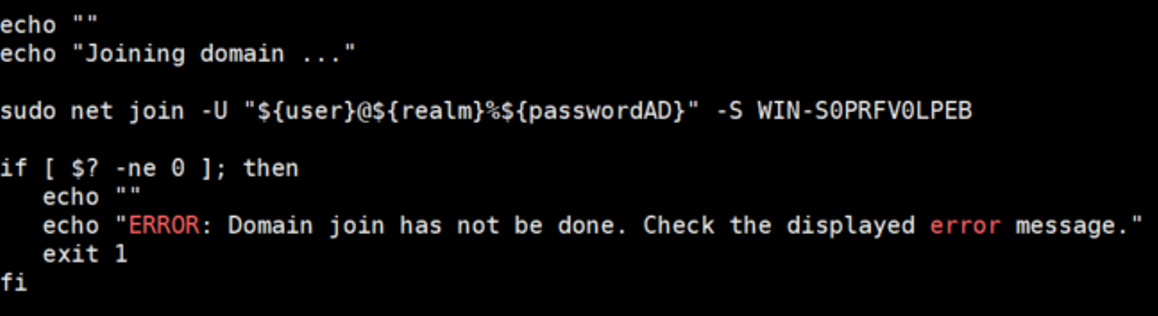
Replace “$ {server}” with the hostname of the AD server. Edit line 183 in the ad_integration.sh file as follows:
/usr/share/opennac/utils/scripts/ad_integration.sh
sudo net join -U "${user}@${realm}%${passwordAD}" -S WIN-S0PRFV0LPEB
Refer to the Active Directory Authentication Server Configurations for advanced configurations.
3.1.10.5.3. Radius Certificate Wizard
The Radius Certificate wizard allows you to configure and generate a CSR (Certificate Signing Request), download it, and finally upload the CRT once signed by the external CA.
Go to Configuration > Wizards > Radius Certificate Wizard to see the following view:
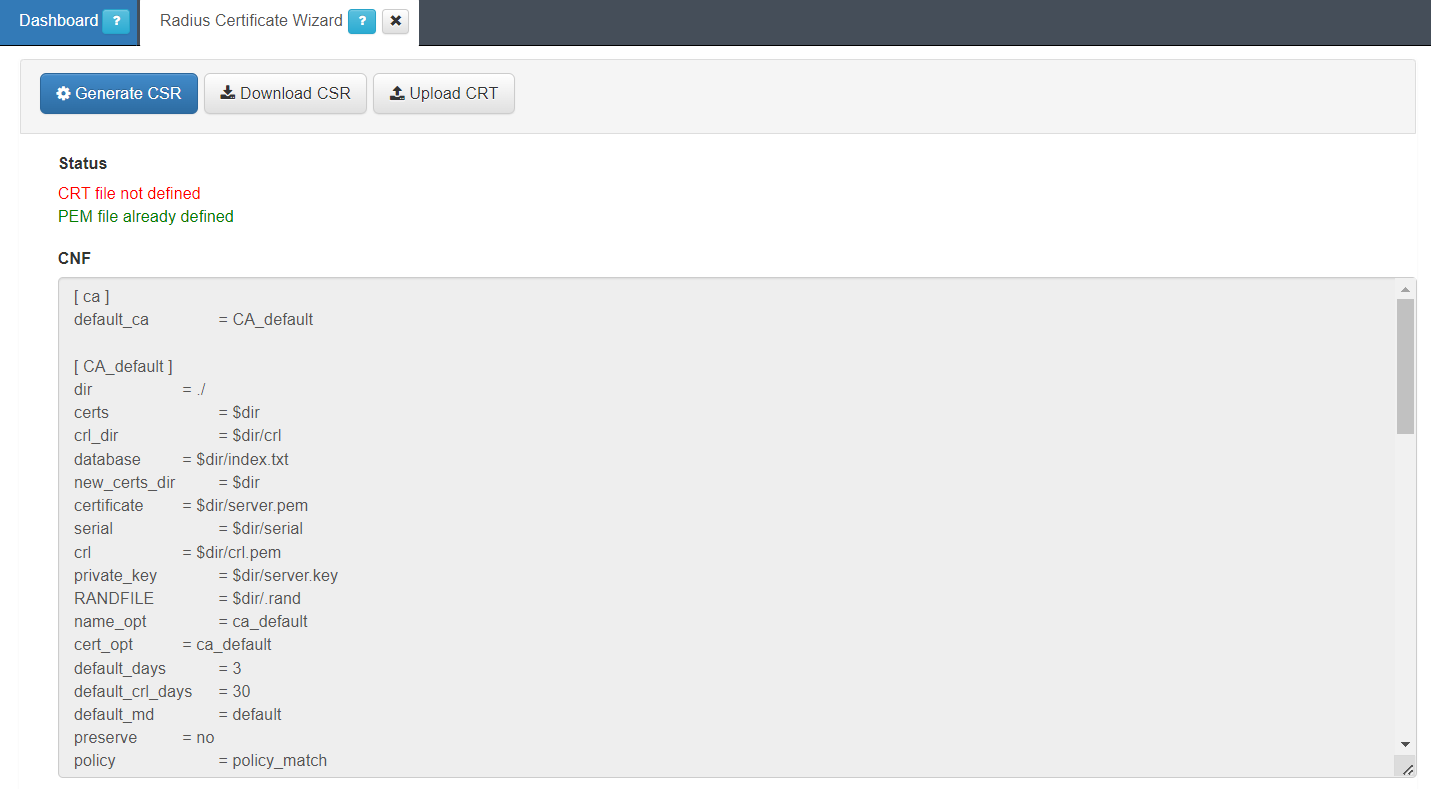
To generate the CSR, click on the Generate CSR button. A window will pop-up so you can fill in the data of the certificate request:
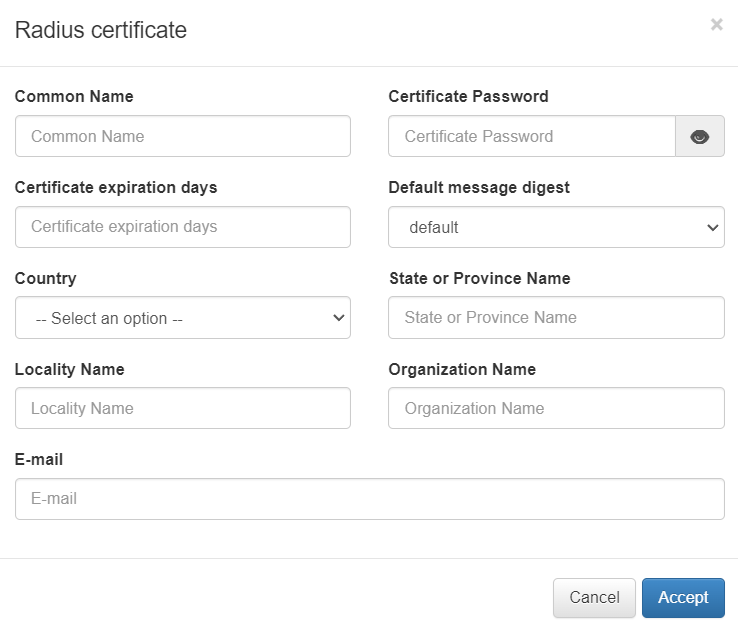
Common Name: Common Name defined in the CSR.
Certificate Password: Password of the generated certificate.
Certificate expiration days: Days until the expiration of the certificate.
Default message digest: CSR encoding type.
Country: Country defined in the CSR.
State or Province Name: Province defined in the CSR.
Locality Name: Locality defined in the CSR.
Organization Name: Name of the Organization of the certificate.
E-mail: e-mail of the certificate.
Once all the fields have been filled in, click on Accept.
Now in the window, we will see the data entered in the [server] section.
At this point, download the CSR file by clicking on the Download CSR button.
Send this CSR file to the administrator of the external CA so they can generate a CRT certificate and sent it back to you.
As soon as you have the CRT certificate, upload it by clicking on the Upload CRT button.