OVERVIEW UNAC¶
1. DEFINITION (What is it?)¶
This use case and the scenarios enables you to control network access in real-time for all your connected assets. openNAC provide the easiest way to implement Authentication, Authorization and accounting policies. openNAC support all the media access such as cable, wifi, vpn and applications providing a centralized network access control system. UNAC support different AAA methods ensuring flexibility and modularity to covert all the customer requiremients supporting major network devices and user devices.
- Authentication can be carried out almost to any modern authentication methods.
- Authorization can be carried out based on assets attributes and its characteristics (Member of in Active directory, security posture, registered in domain…)
- Accounting provides very useful information about user and devices activitis and service use.
UNAC basically is based on a centralized policy engine that allows us to have control over all the assets accesing in the network.
2. MECHANISMS (How does it work?)¶
Universal Network access control use case provide an unified and flexible solution that allows to control all the types of users and devices when connects to the corporative network.
openNAC includes a policy engine that allows to manage any network access request, the flexibility and the control in the policy engine allows us to covert really complex criterias, this policy engine include the following characteristics.
Policy preconditions are:
Time: This allows to select what hours the policy is enabled and then what hours the network access is allowed and active for the end users, an hour time range can be selected.
Users: This component allow us to select users identities to allow or deny network access to the end users, those can be grouped, local and based on remote repositories such as LDAP, AD any many others, authorization is also possible.
User devices: The users devices registered in the openNAC CMDB can be selected by the policy, create groups and use and other system groups can be used as REGISTER DEVICES, UNREGISTERED DEVICES, QUARANTINE DEVICES, also to use TAGGED asset (CDT_CORPORATE_DEVICE, CDT_COMPLIANCE).
Network devices: This allows to manage and control from which network devices are coming network access request, group of network devices can be done to select only wifi, cable, vpn, a location or specific floor.
Sources: Define authentication methods such as (MAB,Supplicant User, Supplicant Host, Supplicant Certificate) and the source of processing events and network requests (VPN, Sensor, Snmp Traps)
The different authentication and authorization methods are flexible to covert customer requiremients:
- Authentication based on username and passwords, EAP methods such as PEAP with AD o LDAP are availables, also local users.
- Authentication based on digital certificates, EAP methods such EAP-TLS with corporate PKI o selfsigned are availables, can be used and validated user certificates and server certificates.
- Authentication based on MAC address, 802.1x MAB method is available.
- Authentication based 2FA such as Google authenticator or Mobileconnect are availables to be used.
- Authentication based on captive portal, is available for BYOD and guest users.
- Authorization based on different criterias.
- AD/LDAP query and attributes.
- Based on the source of the users (wifi, cable, vpn..)
- Based on security posture (compliance, security patches..)
| Clear-text | NT hash | MD5 hash | Salted MD5 hash | SHA1 hash | Salted SHA1 hash | Unix Crypt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAP | OK | OK | OK | OK | OK | OK | OK |
| CHAP | OK | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO |
| DIGEST | OK | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO |
| MS-CHAP | OK | OK | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO |
| PEAP | OK | OK | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO |
| EAP-MSCHAPV2 | OK | OK | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO |
| CISCO LEAP | OK | OK | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO |
| EAP-GTC | OK | OK | OK | OK | OK | OK | OK |
| EAP-MD5 | OK | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO |
| EAP-SIM | OK | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO |
| EAP-TLS | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO | KO |
If the correspoding cell is “OK”, it means that the corresonding password storage method and the protocol are compatible, and that authentication is possible.
If the corresponding cell is “KO”, it means that the corresonding password storage method and the protocol are not compatible, and that authentication is not possible.
Policy postconditions are:
- Set VLAN: Allows to define if network access is provided to the user o NOT, deny access or assign vlans can be configured and easily expanded, for instance service, quarantine, registry, remediation are common examples. openNAC support vlan name and vlan id.
- Voice VLAN: openNAC can manage voIP vlans.
- Security profiles: Allows to deny which access-list are applied to the users, this is done at network layer (switches, ap..) having dynamic and static ones.
- Plugins: Allows to expand openNAC capabilities.
Flexible rule and policy engine is available for the users, rules and its components are intuitive and easy to use.
3. COLLECTED INFORMATION (What do we get?)¶
As soon as the universal network access control module is deployed the following information is gathered about the connected network assets:
TIME: When was the last time the asset connected.
USERNAME: This is the identitity used by the user.
DOMAIN: This is the domain where the user is being registered.
VLAN: The VLAN assigned to the user, this can be VLAN ID or VLAN Name.
Source: Identify authentication methods or source of the information to be processed by the polity engine, for instance 802.1x user and Sensor
IP ADDRESS: IP address assigned to the connected asset.
MAC ADDRESS: Physical asset address.
NETWORK DEVICE IP ADDRESS: IP address of the network devices (switch, AP, VPN) where the asset is connected.
NETWORK DEVICE MAC ADDRESS: MAC address of the network devices (switch, AP,VPN) where the asset is connected on the network.
PHYSICAL PORTS: Interface where the asset was connected and discovered.
TYPE OF DEVICE: Through profiling rules and its discovering mechanisms openNAC can identify the asset type.
MAC VENDOR: Get the vendor assigned to the physical address (Mac address).
TAGS: With plugins such as Discovey and profiling rules it is possible to identify open ports in asset and its type, openNAC uses TAGS to manage all of this information in a flexible way, the TAGs are stroed in the CMDB.
The Tag=”DOP_TCP_9100” means that the asset has the port 9100 TCP open. The Tag=”EPT_PRINTER” means that openNAC has discovered a printer through its profiling rules.
4. DASHBOARD (How do we display what we know?)¶
The information about UNAC can be easily aggregated and use, business profile is one of the best way to get value from openNAC in real time. Business profiles allows you to group policies following same business proposes.
Plenty of information is collected about the users and devices that are under the control of openNAC, business profiles is very useful to have the view about control over network assets.
Access control can be done validating the user identity, at first point with user credentials from local or remote repository, using 802.1x protocol.
OpenNAC allows to have real-time and historical views, dashboards and reports are available to be used and customized.
In some cases there’s no end-point (user devices) with 802.1x supplicant, for this cases administrators can use MAB, this is wide used by devices as printers, cameras, etc.
There are a set of dashboards for UNAC that provide a real view about you security posture regarding network access control.
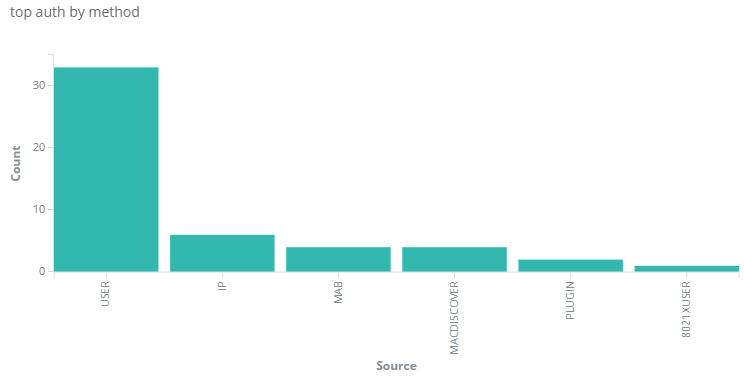
In analytics menu can visualize graphic output for policy rules, the access control is accomplished through access rules, so the matches on each rule is show in graphic format
Also in the first screen is show the top authentication by method.