802.1x¶
802.1X permits or denies device access to the network by using authentication. Ethernet switch ports can be enabled dynamically based on the identity of the device that connects to it. Devices which are not authenticated cannot gain access to the network.
802.1X Authentication Components
- A supplicant : a client device (such as a laptop or endpoint) that attempts to access a LAN/Wireless LAN (WLAN), or the software that runs on this device and that provides credentials to the authenticator.
- An authenticator : a network device (such as an Ethernet switch or wireless access point) that acts as an access point to a protected network. For 802.1X authentication, the supplicant provides network credentials, such as username, password, digital security certificate, or a combination of these, to the authenticator. The authenticator then forwards the credentials to the authentication server for verification.
- An authentication server : a server (such as openNAC Core) that guards the protected network. For 802.1X authentication, the authentication server receives the supplicant’s network credentials from the authenticator and verifies the supplicant’s identity. Then the supplicant is able to access the resources located on the network.
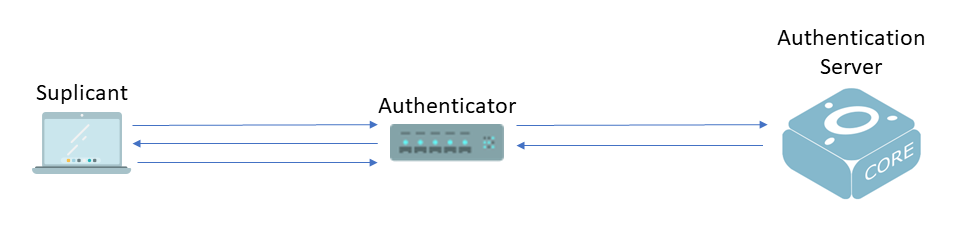
802.1 is based on RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service) protocol which consist in a standardized method of information exchange between a device that provides network access to users called RADIUS client and a device that contains authentication information for those users called RADIUS server.