1.4.3. Segmentation
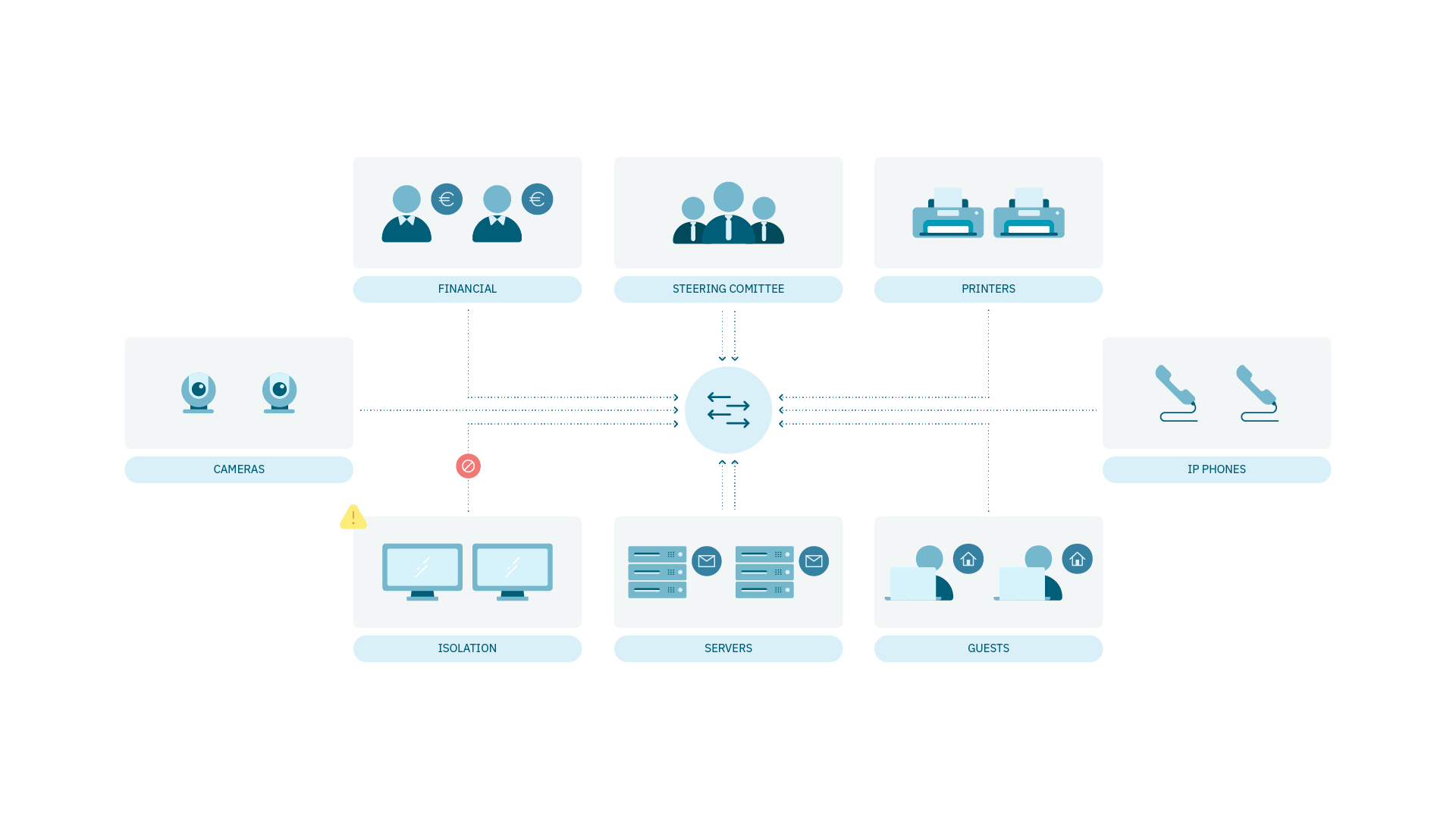
The Segmentation module enhances security and performance by dividing the corporate network into smaller, isolated segments, each with its own security policies and access controls.
This allows for precise control over traffic flow, limiting it by type, source, and destination. The strategy used to implement segmentation is known as a segmentation policy.
Network segmentation can be implemented in various ways to maximize infrastructure benefits. It integrates different network components to strengthen authentication and authorization, helping to protect critical assets against advanced threats. Additionally, it automates security incident responses and enforces policy-based controls over business-critical assets.
Note
The Segmentation module relies on the UNAC module, meaning its functionality may depend on the configuration and performance of UNAC.
1.4.3.1. Segmentation and Firewall
Segmentation and firewall are complementary, not mutually exclusive.
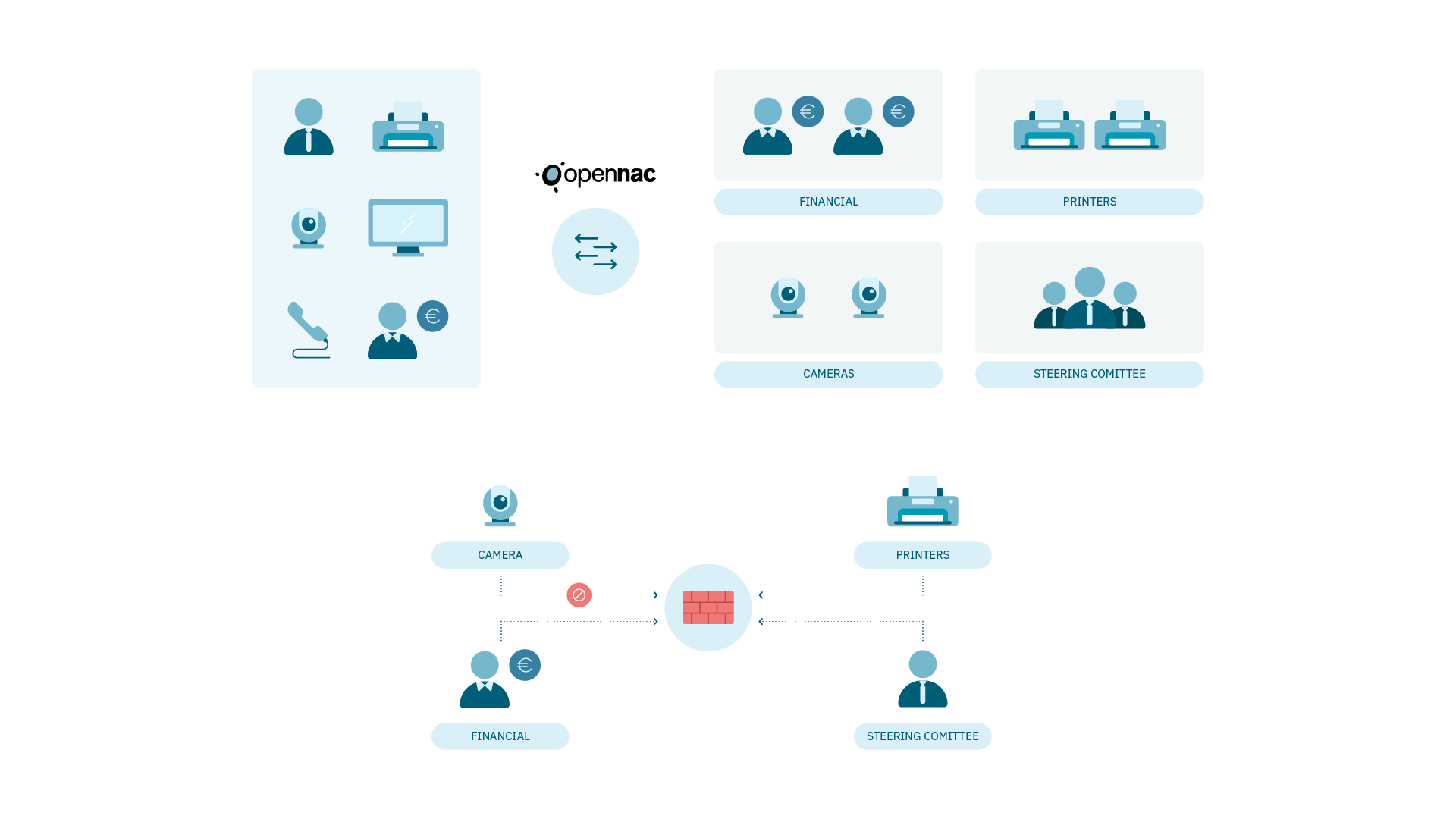
Segmentation automatically defines in which group (addressing) users/devices are assigned according to certain input parameters such as typology, profile, position, role, location, etc.
The firewall determines the traffic that flows between the groups assigned by the segmentation, the flows between the network segments.
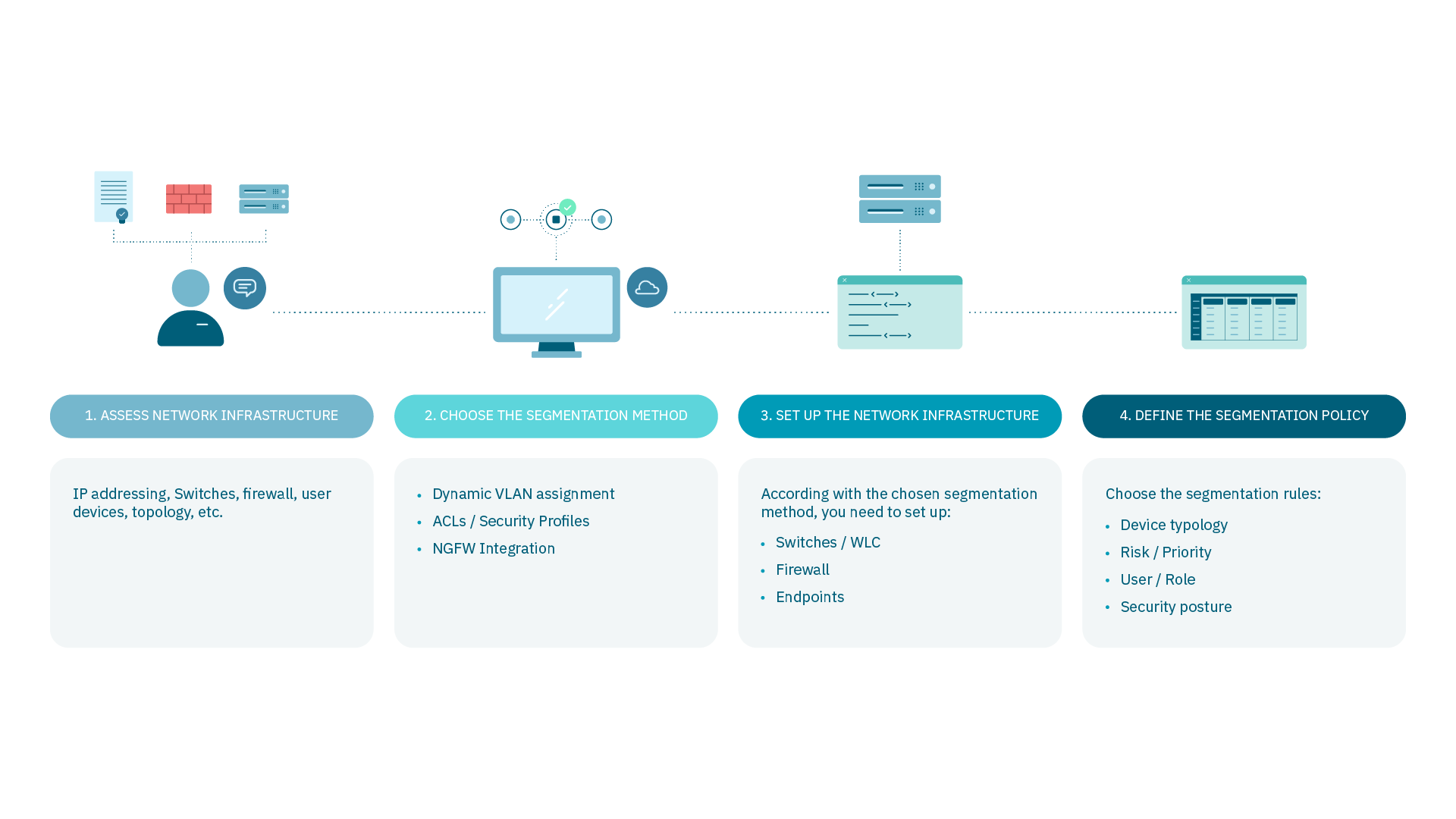
1.4.3.2. Segmentation in 4 Steps
The proposal of this module can be summarized in 4 simple steps:
1.4.3.3. Segmentation Methods
There are different methods that enables network segmentation:
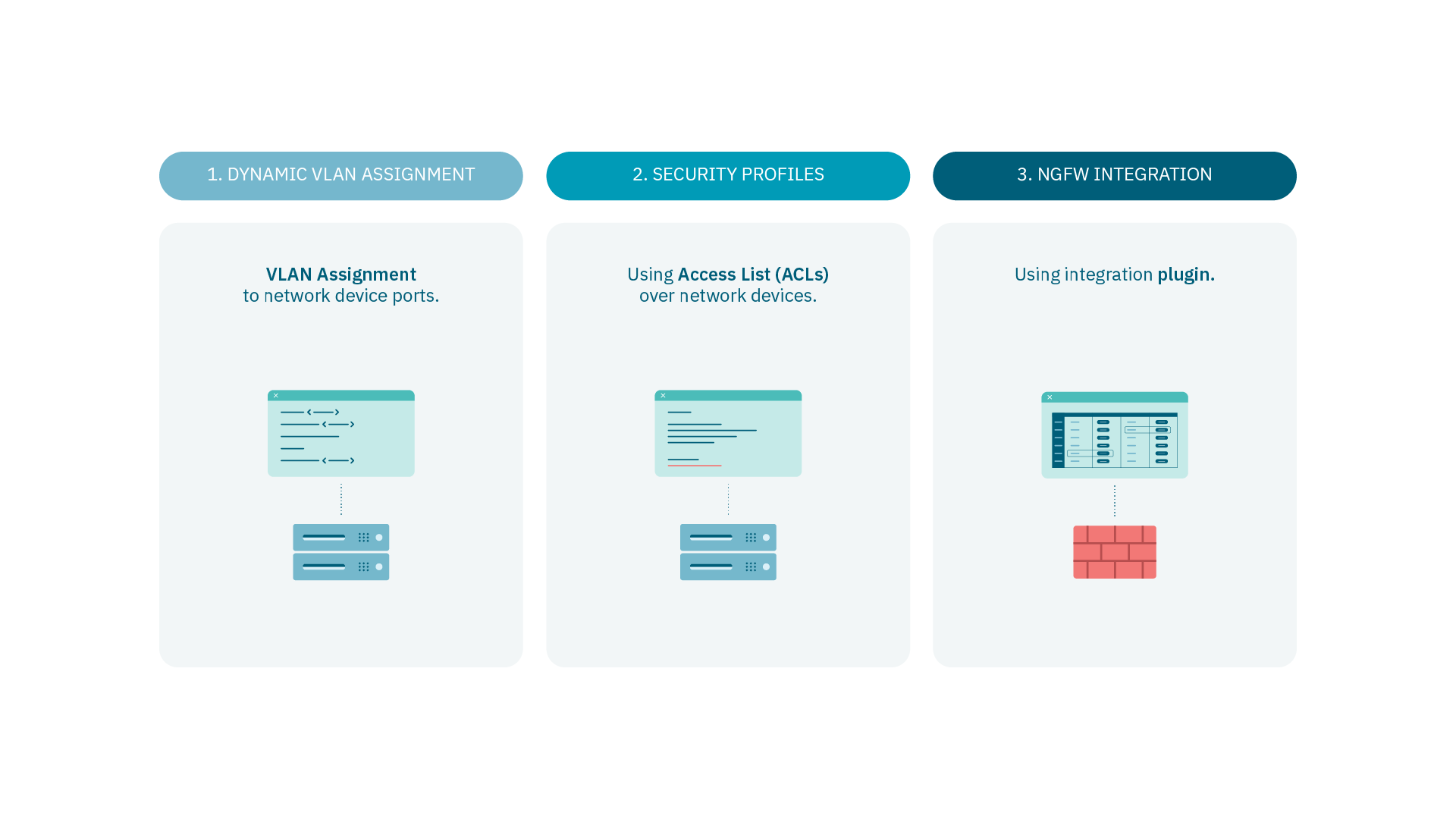
Dynamic VLAN assignment: VLAN Assignment to network device ports.
Security Profiles: UsingAccess List (ACLs) over network devices.
NGFW Integration: Using an integration plugin.
1.4.3.3.1. Dynamic VLAN assignment
Using RADIUS parameters to send VLAN identifiers information, the Switch configures its network interfaces where devices are connected.
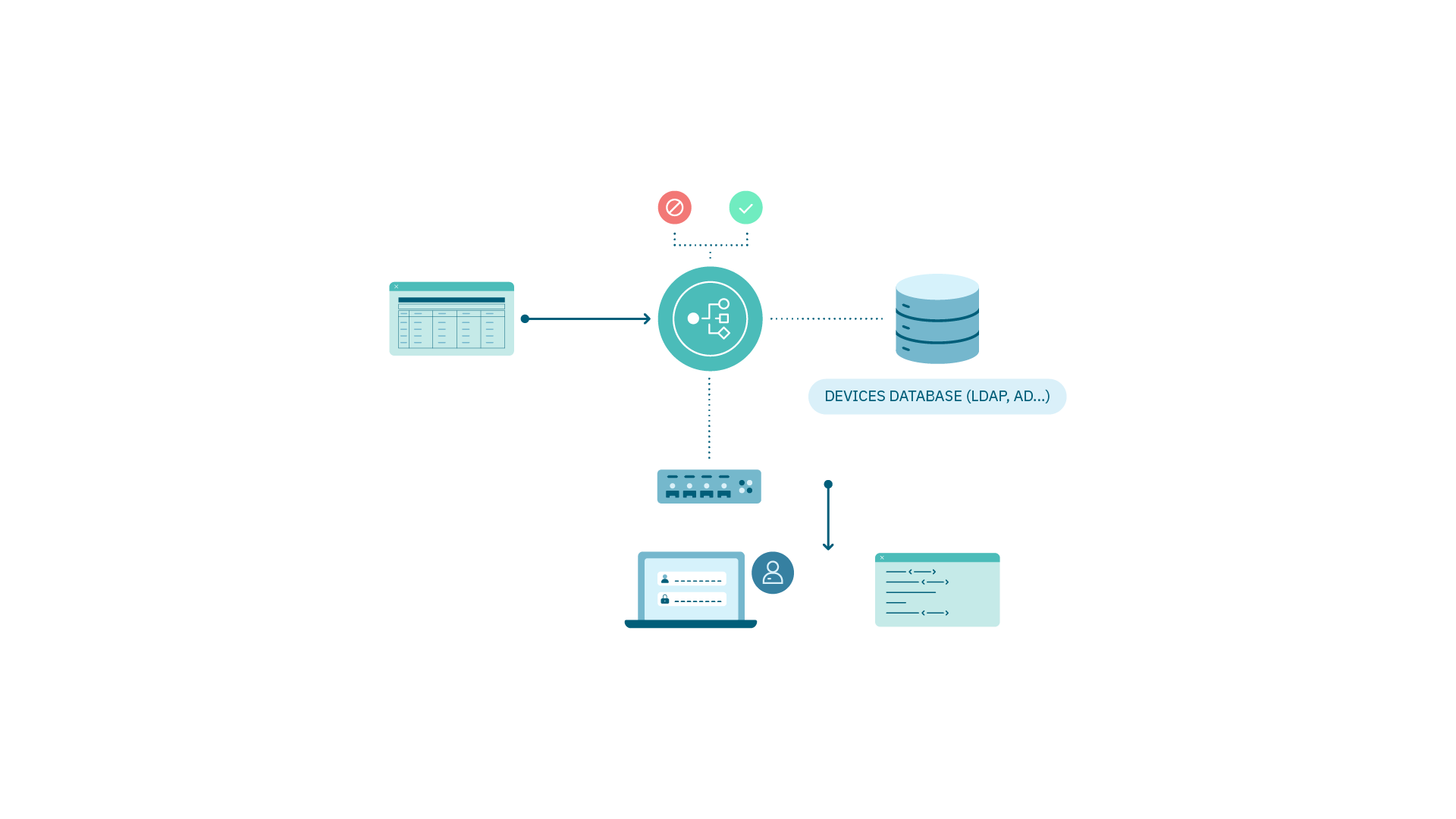
Requirements
802.1X protocol configuration on network device.
VLANs and IP addressing Access.
Segmentation policy in OpenNAC Enterprise.
Supplicant Configuration on User Device, MAB for devices without a supplicant.
Note
To use role/user in preconditions, integration with a user database (e.g., LDAP or AD) is required.
1.4.3.3.2. Security Profiles (ACLs)
It is an access control list (ACL) that can be assigned to any network device interface where users access network.
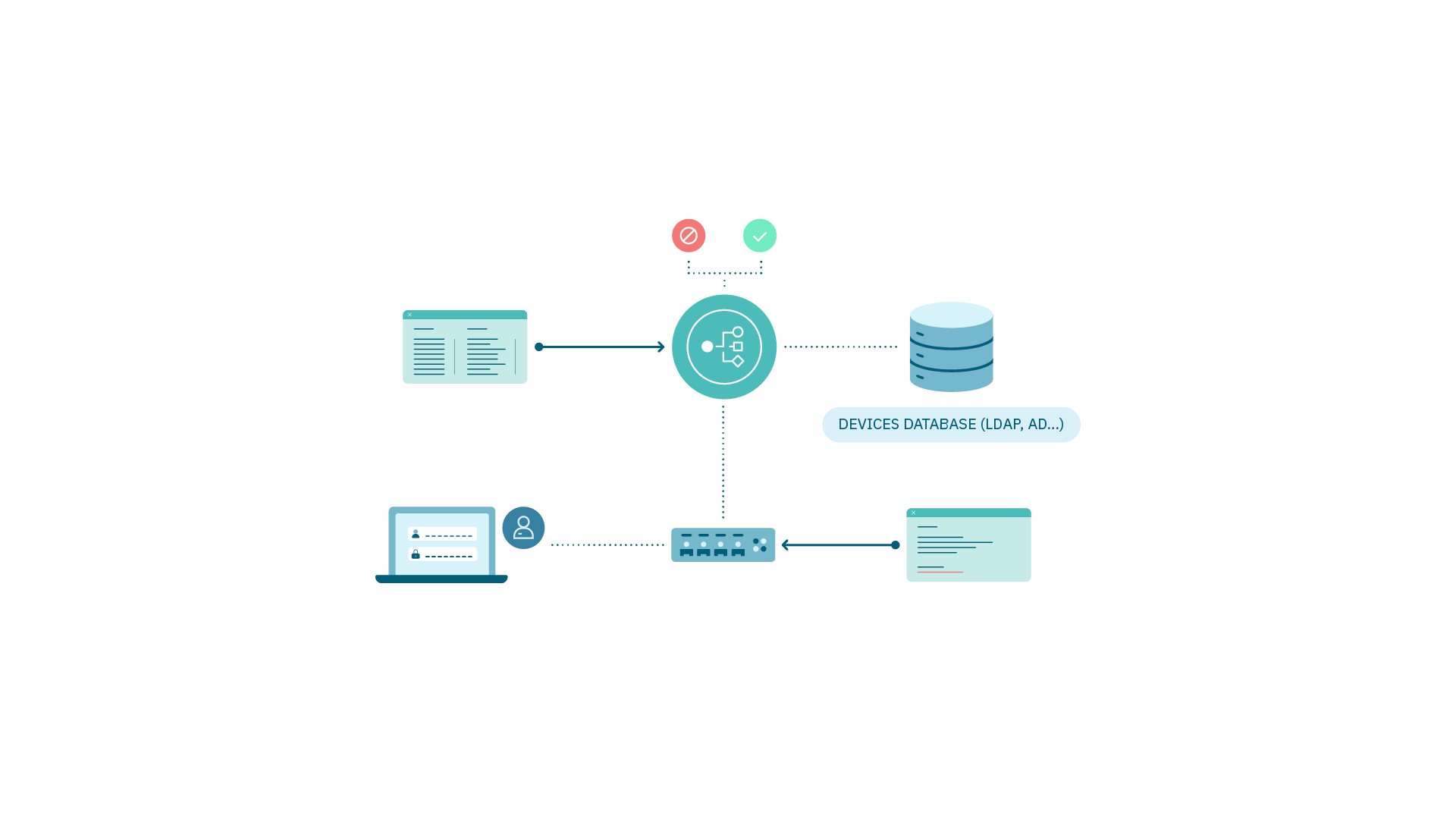
There are two types:
Static: To apply the ACL, it must be previously configured in the switch and then applied.
Dynamic: Through a command the ACL is created and applied. It must not previously exist.
Requirements:
Configuration of Security Profiles (ACLs)
Switch (static)
OpenNAC E(Dynamic)
802.1X protocol configuration on network device.
Segmentation policy in OpenNAC Enterprise.
Supplicant Configuration on User Device, MAB for devices without a supplicant.
Note
To use role/user in preconditions, integration with a user database (e.g., LDAP or AD) is required.
1.4.3.4. NGFW Integration
It is done through a plugin where we can send information from the system to the firewall to apply access control policies.
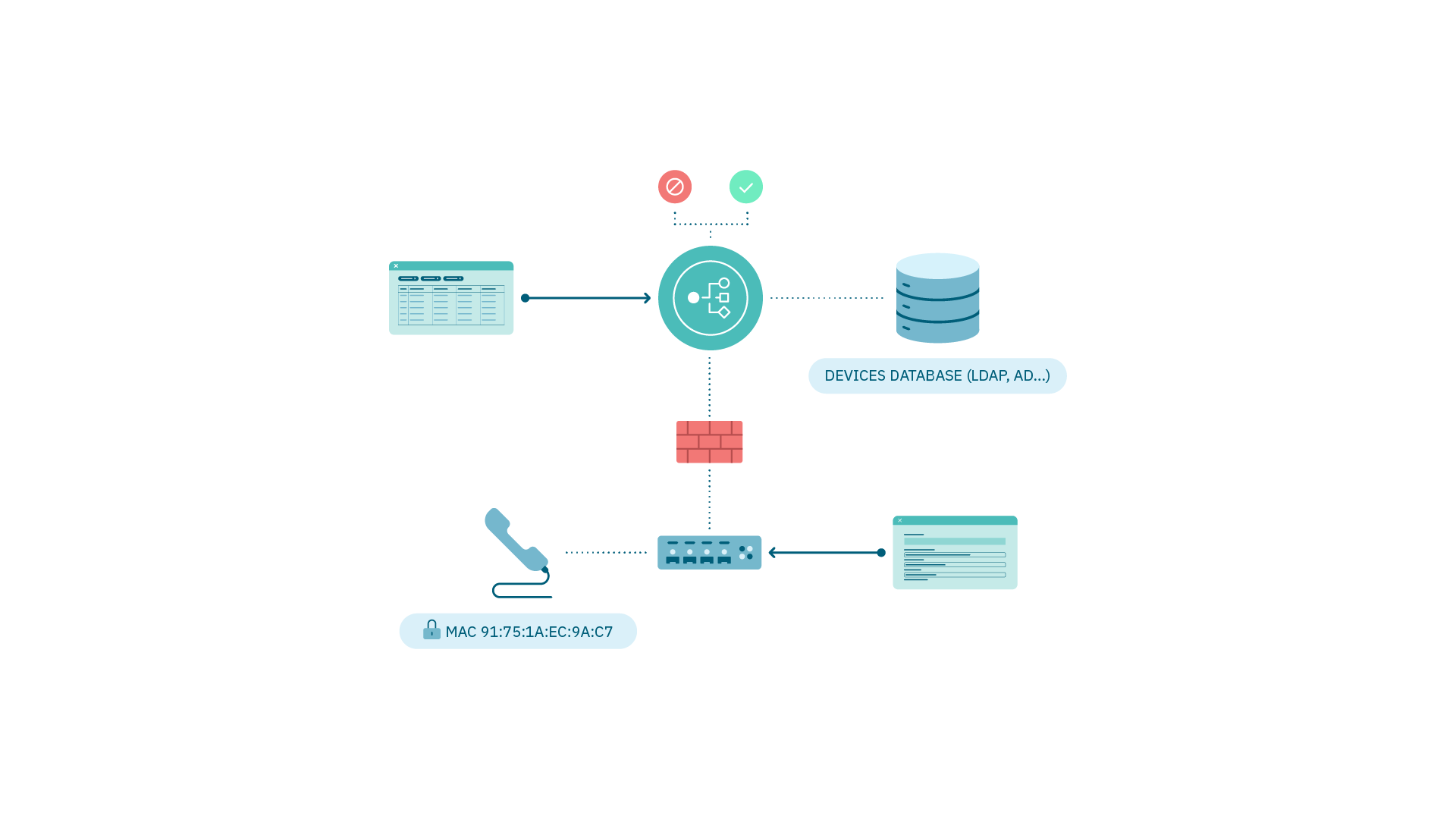
Requirements:
Plugin activation and configuration.
Access rule (segmentation) in OpenNAC Enterprise.
Communication via API with the NGFW.
Note
To use role/user in preconditions, integration with a user database (e.g., LDAP or AD) is required.
1.4.3.5. Dashboards Customization
All devices, their characteristics, and data collected by OpenNAC Enterprise are stored in the ON CMDB. Every characteristic is represented by TAGS. This structure can be read and generate value in different ways according to the requirements or objectives of each company.

The administrator selects the visualization type to set the Dashboard graphics (Bars, cake, etc.).
Select the information and the device data (TAGS) that you want to show from the CMDB.
Set the structure of dashboards and select all visualization.
Generate a new dashboard by adding all the visualizations you want.
Add the dashboard to the OpenNAC Enterprise Administration Portal.
The next section will outline the deployment steps required for the Segmentation use case.