4.3.1. Introduction
On this page we will introduce the Segmentation use case, going through its explanation, benefits, steps and sources.
4.3.1.1. What is Segmentation?
Segmentation divides a corporate network into smaller parts, improving security and performance. In a segmented network is possible to control how the traffic flows, and limit the flow by traffic type, source, and destination, among other options. The strategy you decide to segment the network is called a segmentation policy. Segmentation is an OpenNAC Enterprise module that allows automatic network segmentation and isolation based on different input parameters.
The submarine compartment analogy is an accurate representation of the segmentation concept:
This corporate network segmentation can be carried out in different ways to maximize the benefit of the infrastructure. It articulates different components of the network to increase authentication and authorization actions.
Network segmentation helps to protect your critical assets against advanced threats. Enhance the security incident respond process automatically and limit actions over business critical assets via policy-based network segmentation.
This module is applied based on the UNAC module, so the operation of the segmentation may be conditioned by the configuration and operation of the UNAC module.
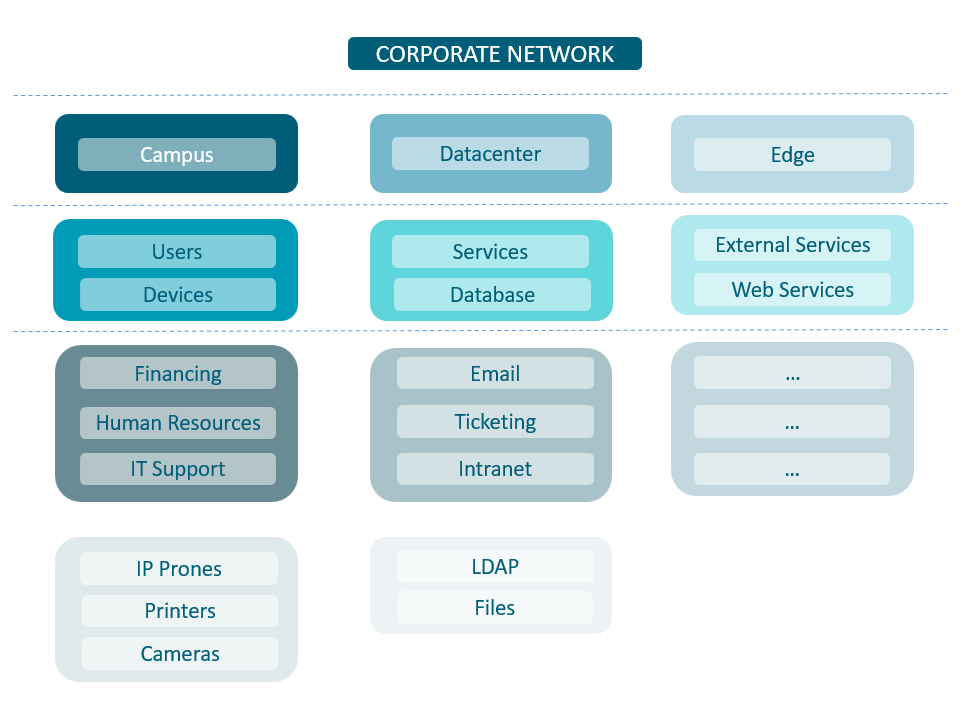
4.3.1.2. Is network segmentation necessary if I already have a firewall?
Segmentation and firewall are complementary, not mutually exclusive.
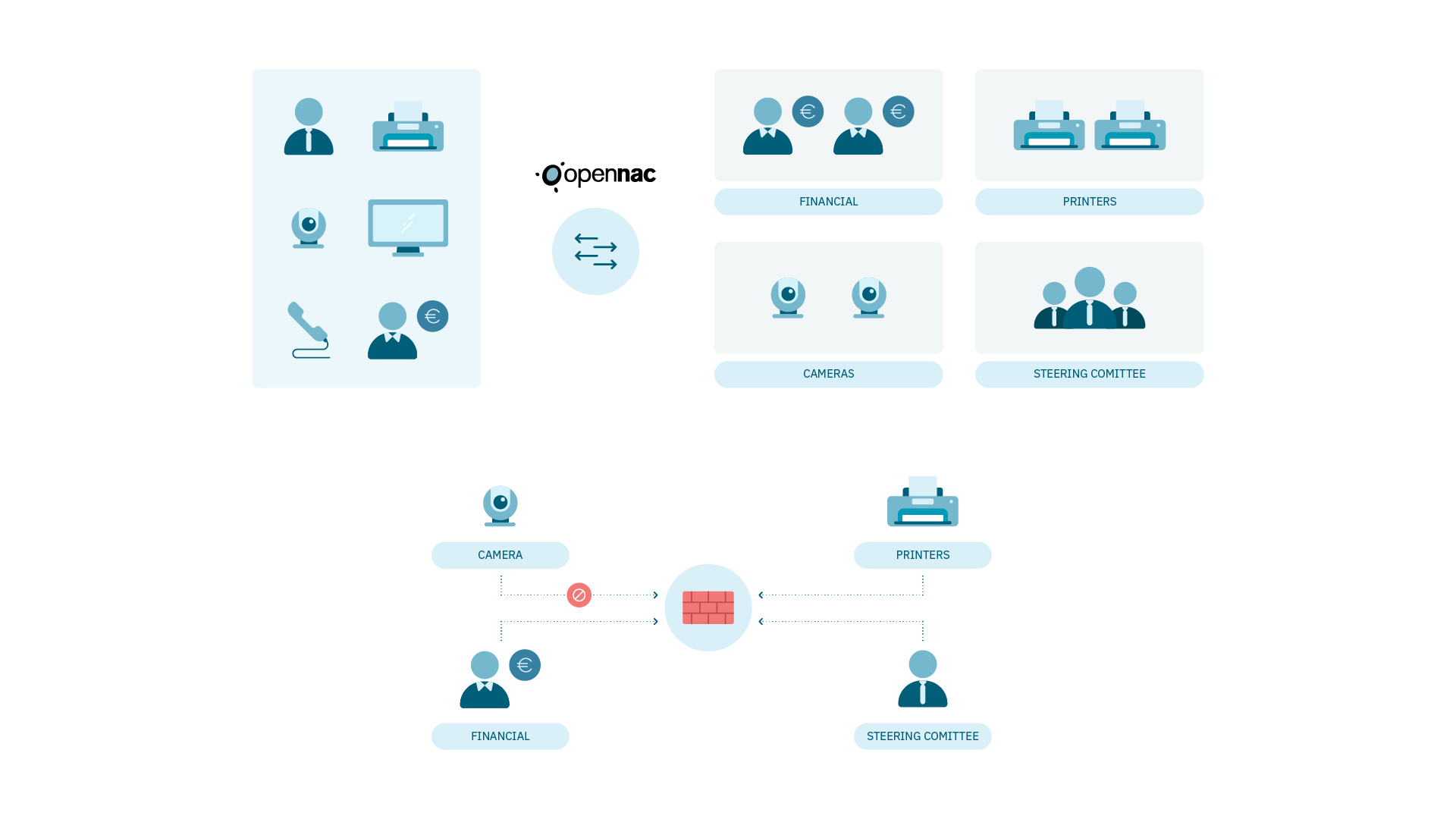
Segmentation automatically defines in which group (addressing) users/devices are assigned according to certain input parameters such as typology, profile, position, role, location, etc.
The firewall determines the traffic that flows between the groups assigned by the segmentation, the flows between the network segments.
4.3.1.3. Segmentation Benefits
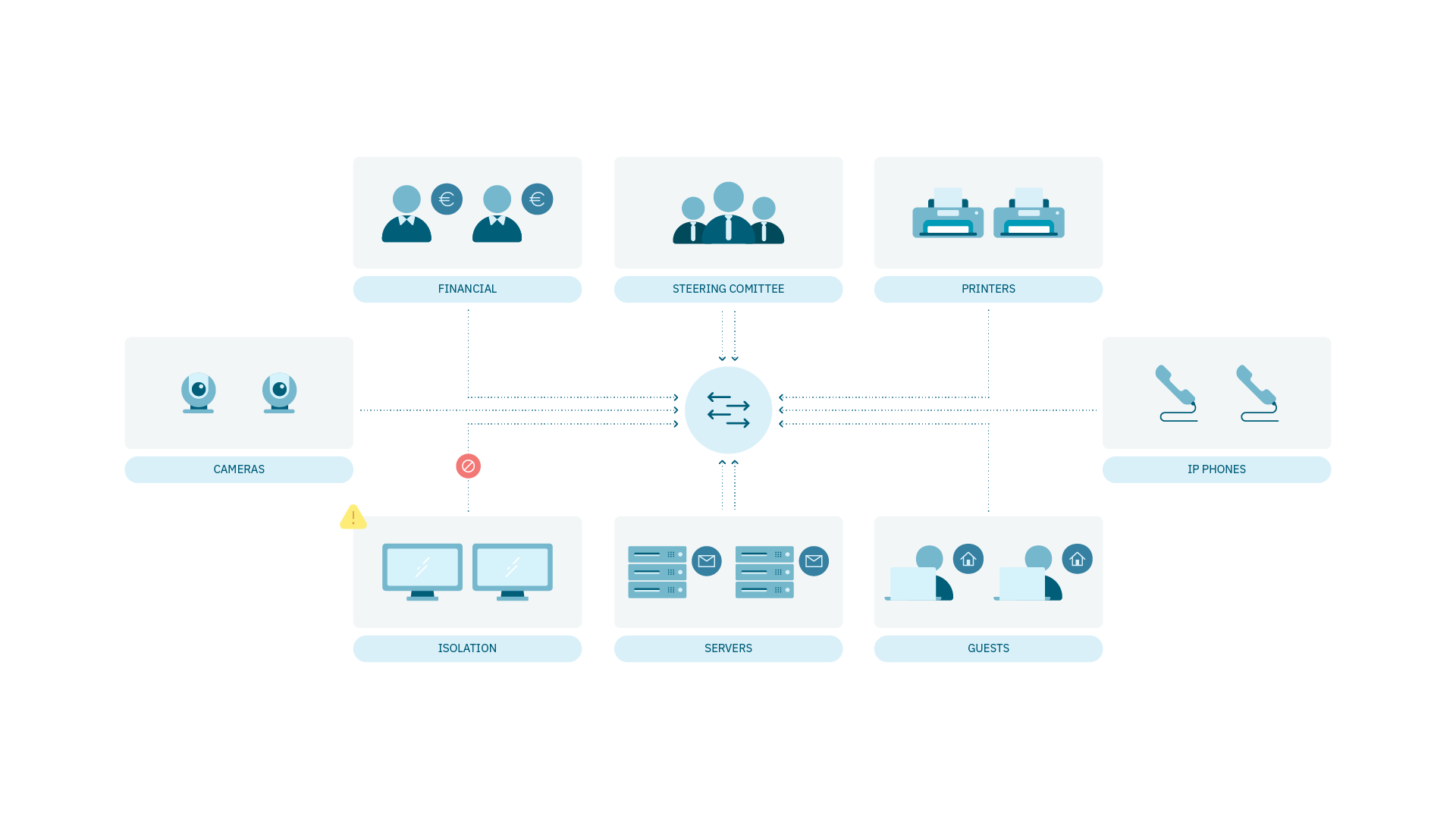
Set foundations for attack surface management: Group devices for effective risk management and network growth.
Limit cyberattack incidents damage: Divide the entire network into small and logically separated segments, reducing the attack surface.
Automatic secure network growth: Once policy segmentation is deployed, all the network connections will automatically fit into defined segments.
User/Device isolation: Through the definition of security posture for user devices or isolate assets by demand in a security incident.
Maximize the value of your network infrastructure by integrating with network platforms for securing and stablish the segmentation.
Deploy the least privilege principle by controlling how traffic flows among the network segments.
Facilitates the standards and frameworks adoption such as ISO2700x, NIST, ENS etc.
4.3.1.4. Segmentation in 4 Steps
The proposal of this module can be summarized in three simple steps:
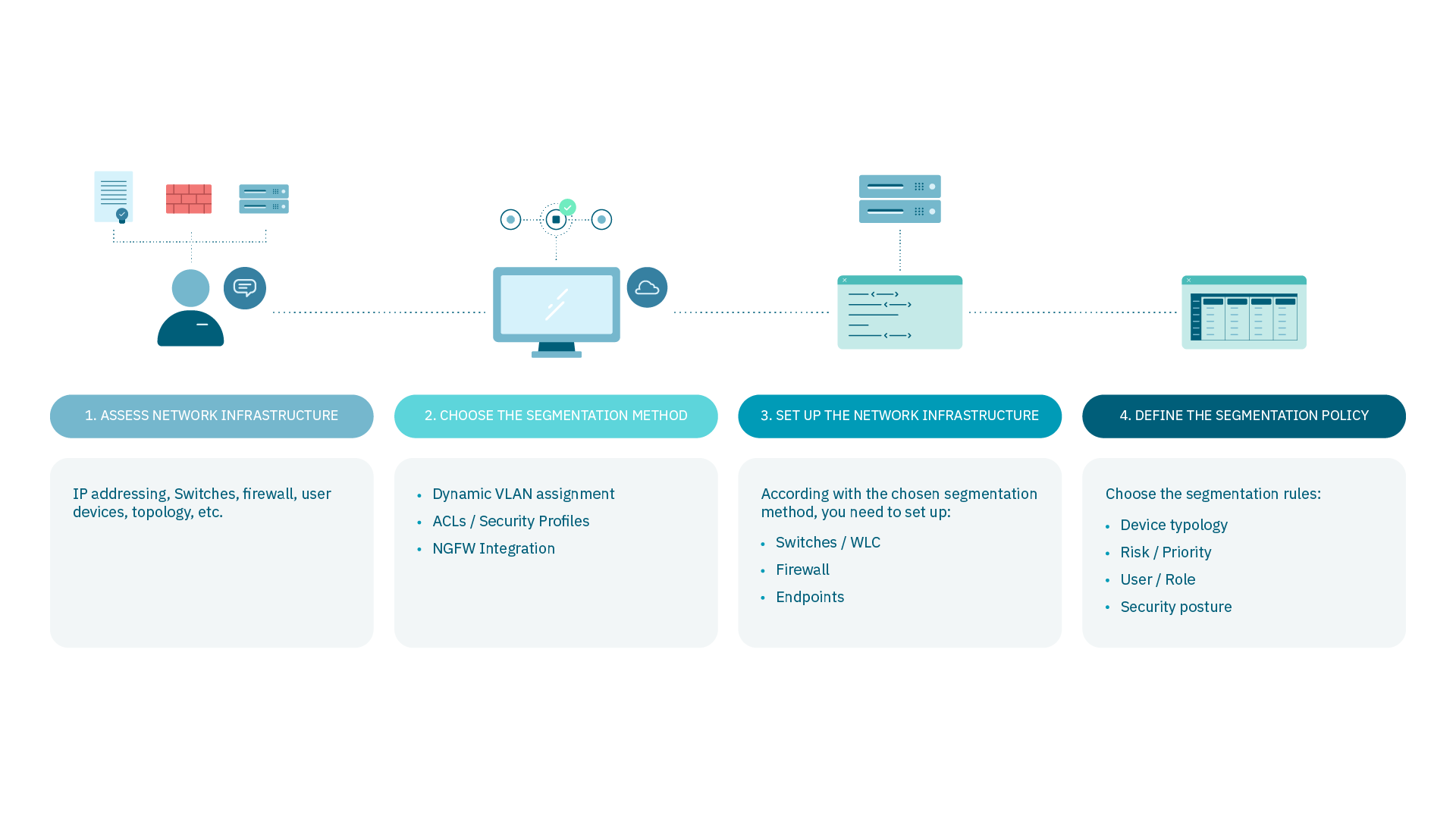
Once inside, all connections from all devices made on the network send different attributes to OpenNAC Enterprise.
OpenNAC Enterprise evaluates the attributes of each connection. Based on each evaluation result, it assigns a network segment or takes actions toward the connection.
The connection is assigned to a network segment or to a certain group that is associated with the relevant permissions and access.
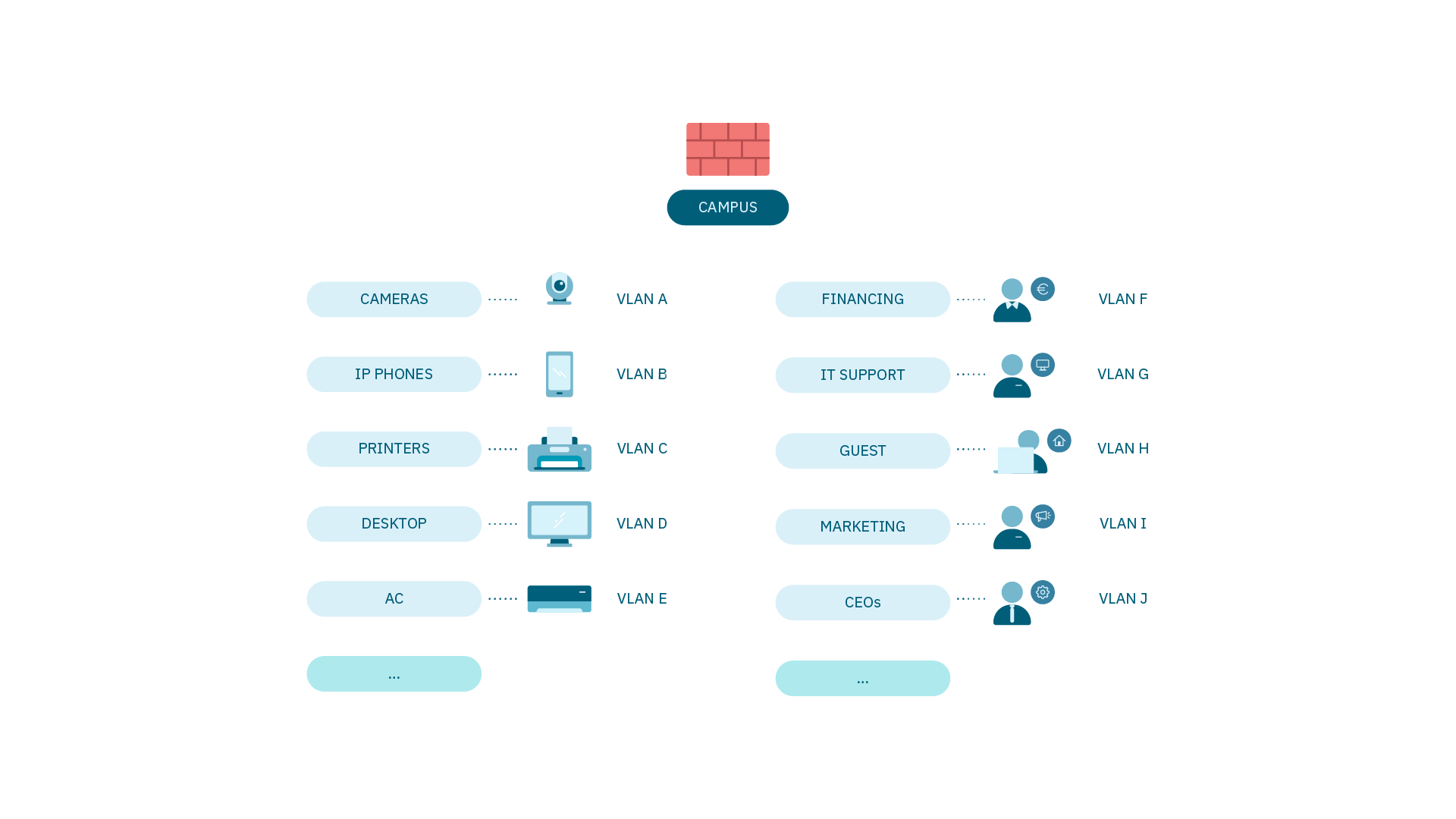
4.3.1.5. Segmentation Methods
We have different methods that allow us to segment our network:
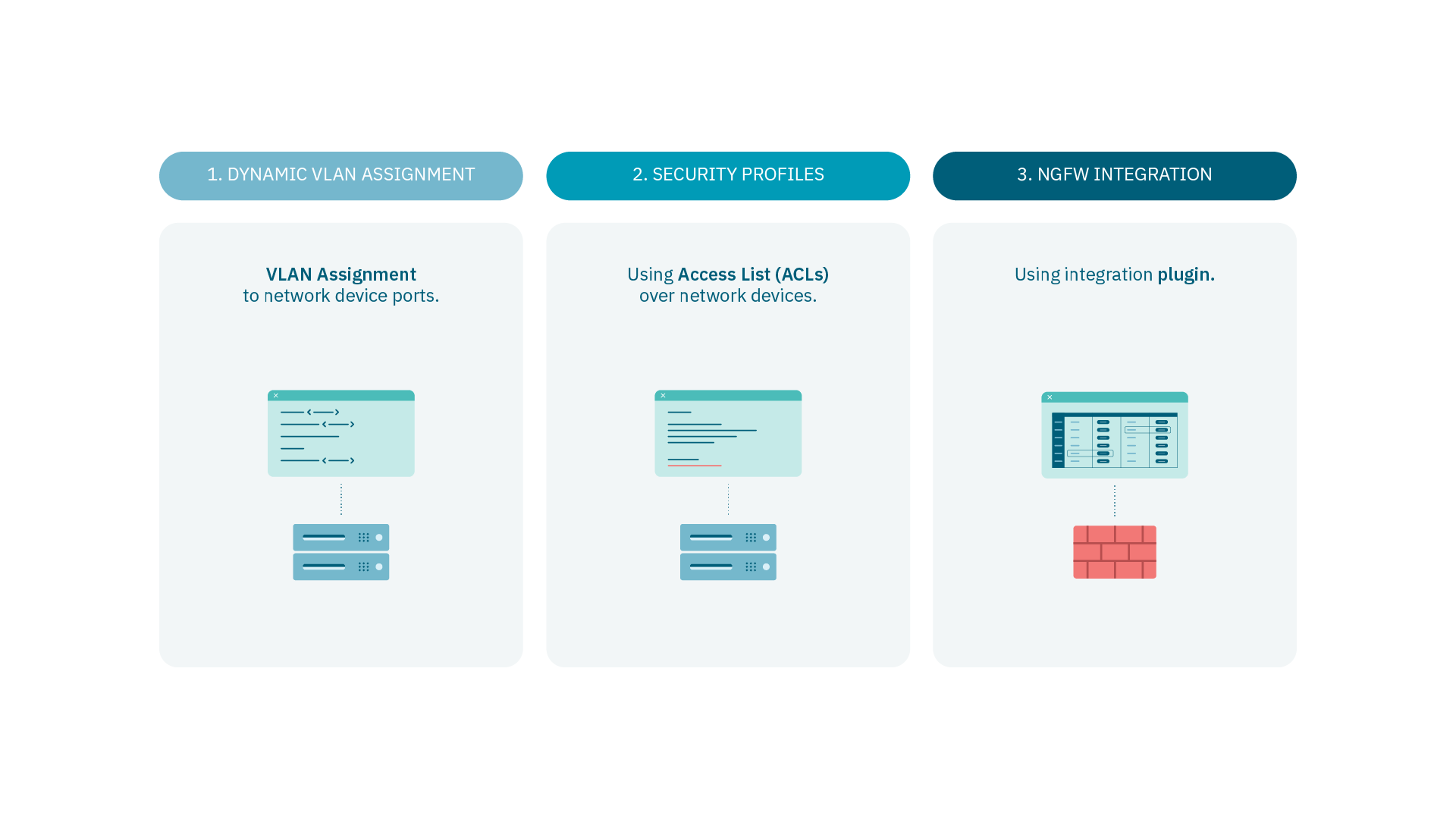
Dynamic VLAN assignment
VLAN Assignment to network device ports.
Security Profiles
UsingAccess List (ACLs) over network devices.
NGFW Integration
Using an integration plugin.
4.3.1.5.1. Dynamic VLAN assignment
Using RADIUS parameters to send VLAN identifiers information, the Switch configures its network interfaces where devices are connected.
Requirements
802.1X protocol configuration on network device.
VLANs and IP addressing Access.
Segmentation policy in OpenNAC Enterprise.
Supplicant Configuration on User Device, MAB for devices without a supplicant.
NOTE: to use role/user in preconditions Integration with User Database (LDAP, AD).
4.3.1.5.2. Security Profiles (ACLs)
It is an access control list (ACL) that can be assigned to any network device interface where users access network.
There are two types:
Static: To apply the ACL, it must be previously configured in the switch and then applied.
Dynamic: Through a command the ACL is created and applied. It must not previously exist.
Requirements:
Configuration of Security Profiles (ACLs)
Switch (static)
OpenNAC E(Dynamic)
802.1X protocol configuration on network device.
Segmentation policy in OpenNAC Enterprise.
Supplicant Configuration on User Device, MAB for devices without a supplicant.
NOTE: to use role/user in preconditions Integration with User Database (LDAP, AD).
4.3.1.5.3. NGFW Integration
It is done through a plugin where we can send information from the system to the firewall to apply access control policies.
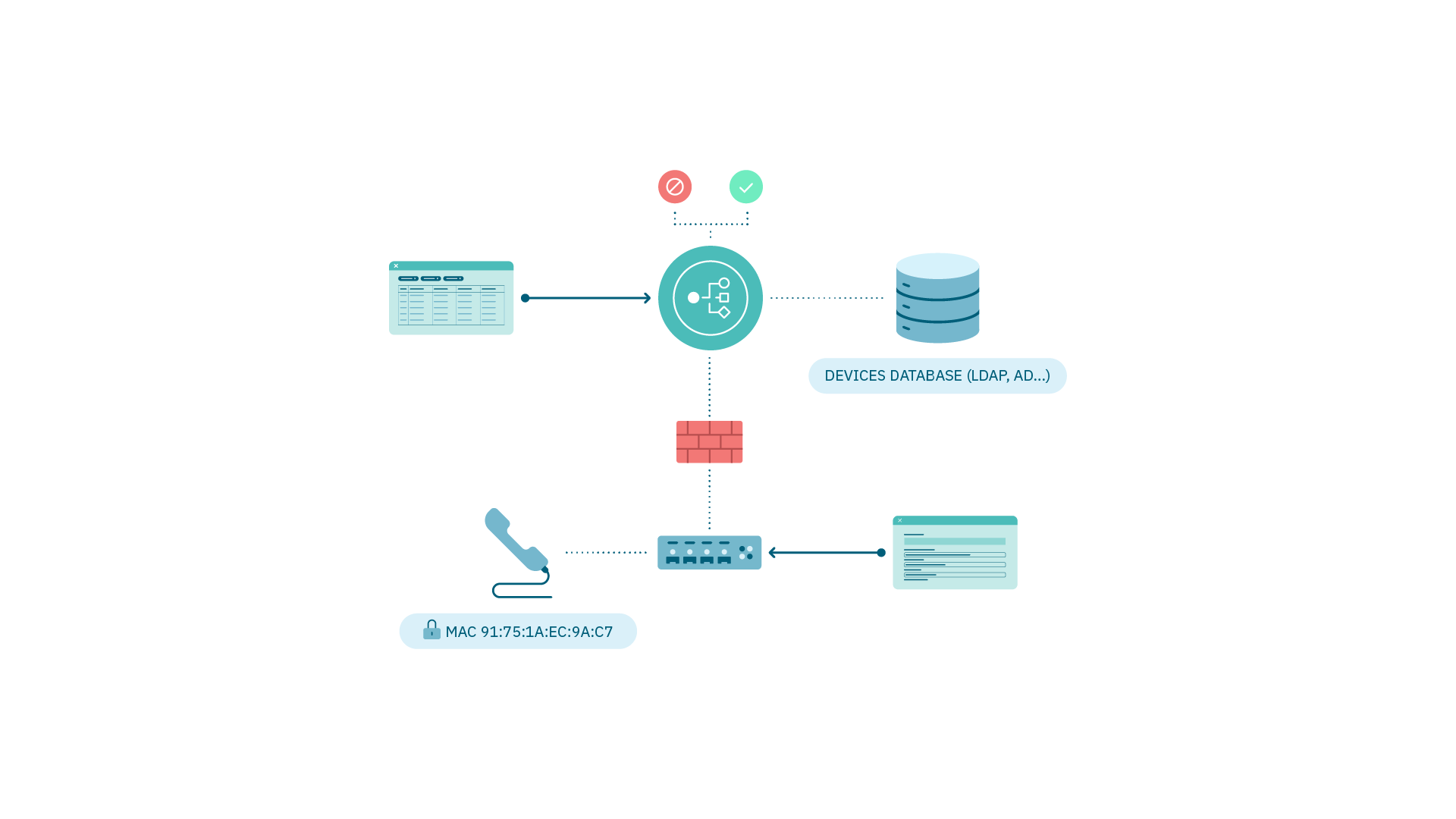
Requirements: - Plugin activation and configuration. - Access rule (segmentation) in OpenNAC Enterprise. - Communication via API with the NGFW.
NOTE: To use role/user in preconditions integration with user Database (LDAP, AD).
4.3.1.6. Segmentation Value
4.3.1.6.1. IT Support/ Help Desk
Reducing incidents’ response time (CAO): Identify the affected device from the CMDB (username, IP, MAC, etc.) and toggle the related port on the switch (Toggle Port).
4.3.1.6.2. Monitoring - IT management
Real time connections information Control Dashboards.
Users’ connection metrics:
Users by functional area
Users location
Devices Information:
Device topology
Device location
Device information
MAC
Vendor
4.3.1.6.3. Adaptability
Easy integration with corporative infrastructure.
The value is subjective. The perception of the value of an IT tool increases as it solves a given problem.
The adaptability degree of IT tools will determine the value they provide.
The Segmentation module integrates with the current company’s infrastructure. It does not add administration efforts, but rather automates some recurring tasks, removing some mechanical task from the technical team.
Eliminate technological rigidity
Task automation
Multi-vendor, agnostic technology
Plugins, integrations
4.3.1.6.4. Dashboards Customization
All devices, their characteristics, and data collected by OpenNAC Enterprise are stored in its CMDB. Every characteristic is represented by TAGS. This structure can be read and generate value in different ways according to the requirements or objectives of each company.

The administrator selects the visualization type to set the Dashboard graphics (Bars, cake, etc.).
Select the information and the device data (TAGS) that you want to show from the CMDB.
Set the structure of dashboards and select all visualization.
Generate a new dashboard by adding all the visualizations you want.
Add the dashboard to the OpenNAC Enterprise web console.
4.3.1.6.5. Reports. Audit Teams.
Management and audit reports in real time:
Companies can choose how to segment authenticated users on the network to have a report available at any time.
Examples:
Authenticated users
Authentication sources
Connected users from a certain group
Users location
To continue with the Segmentation module, read the next section Segmentation Architecture.