4.2.1. Introduction
On this page, we will see the use case of UNAC. This includes an explanation of what UNAC is, the benefits UNAC brings, the value it adds, and simple use-case scenarios.
4.2.1.1. What is UNAC?
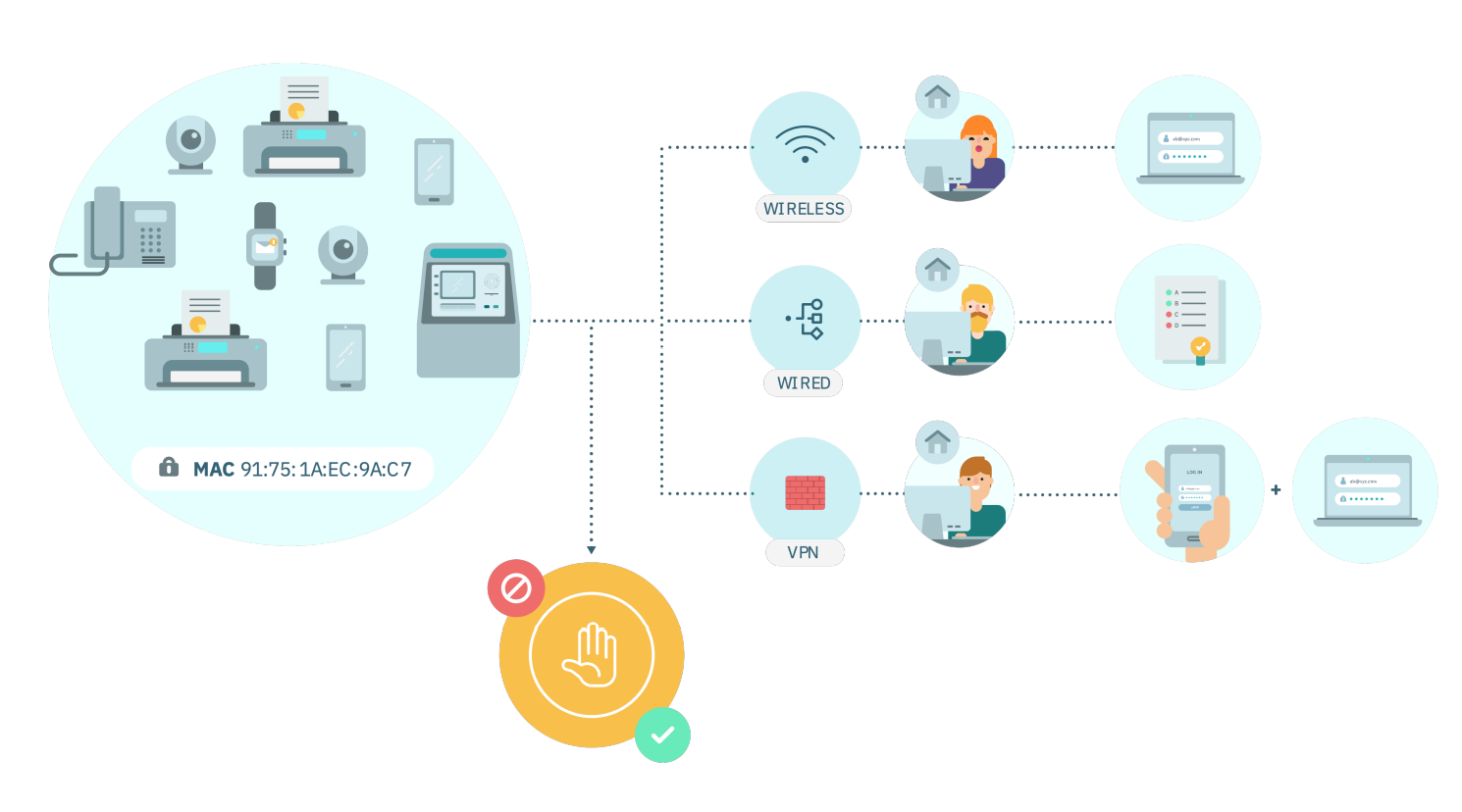
OpenNAC Enterprise is a module with the power to authenticate all users and devices in a corporate network (wired, wireless, and VPN).
Allows you to set:
The foundations of Zero Trust security strategy.
The security principles as the least privilege principle.
Allows users and/or devices authentication through:
Corporate user credentials
Corporate credentials + OTP. (2FA)
Certificates with internal CA
MAB for non-supplicant devices
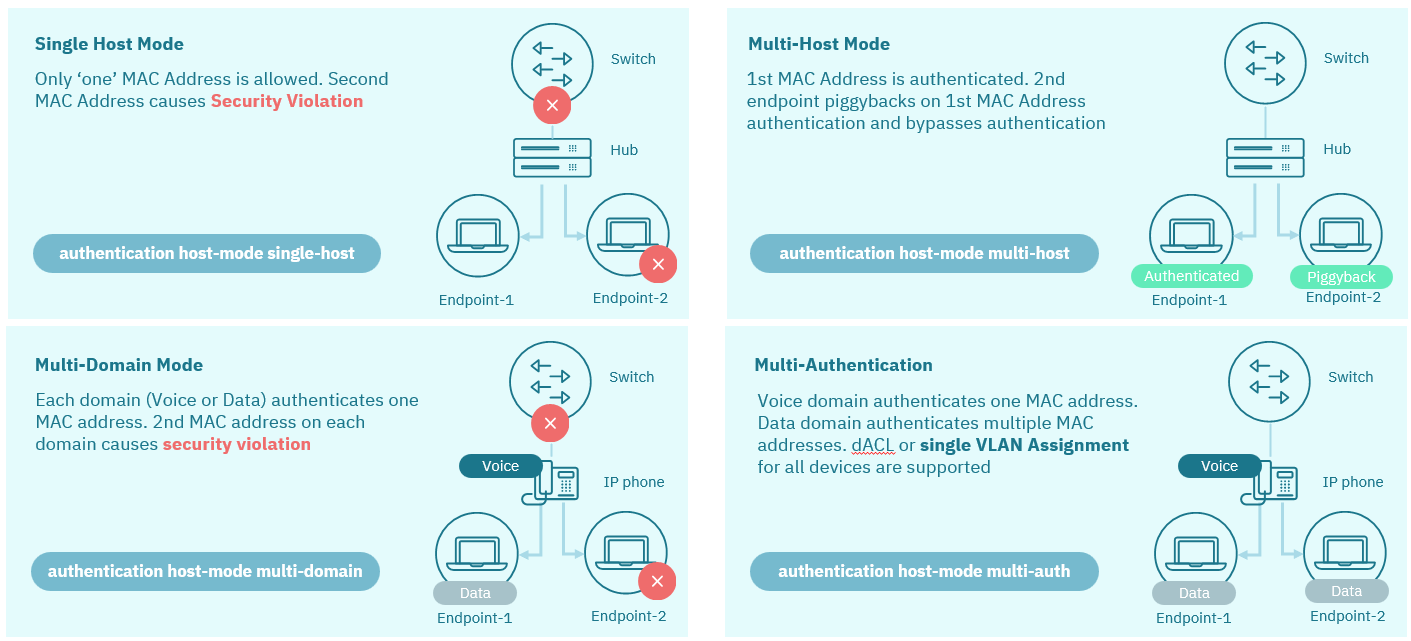
802.1X protocol as the basis for establishing authentication policies. T understand the protocol fundamentals, see 802.1x Basic Concept
4.2.1.2. UNAC Benefits
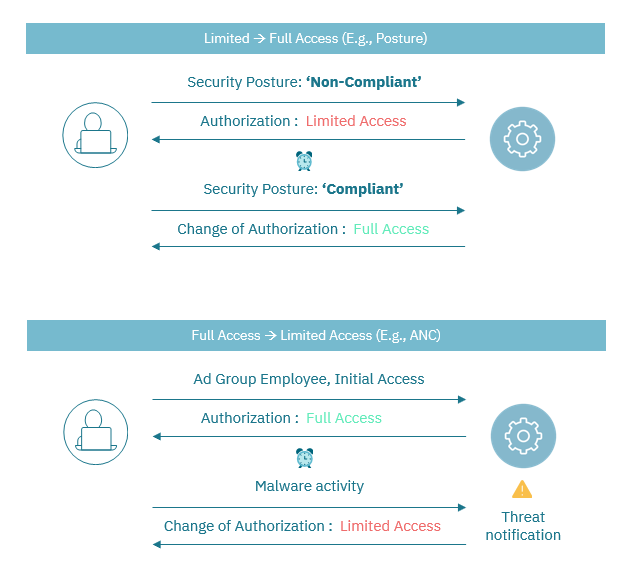
Establishes the foundations of the Zero Trust strategy, through the user’s identity validation and the entity of devices, mitigating the risk of identity fraud.
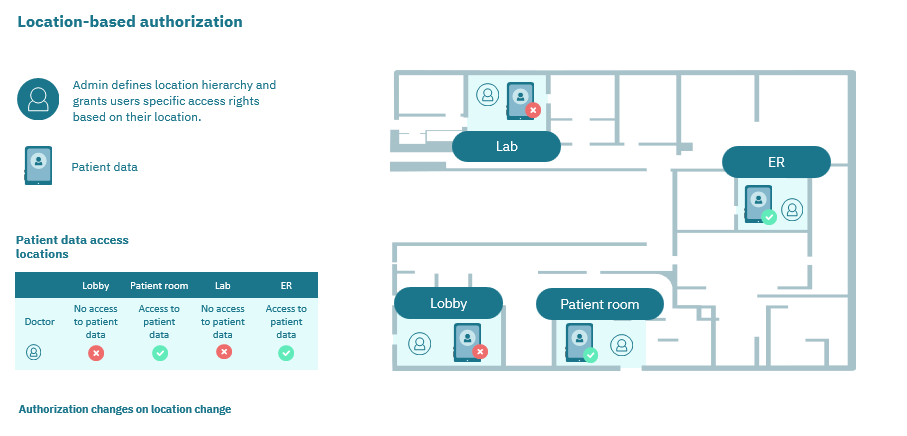
Allows to setting up security principles, determining the identity of the users, and granting only the necessary permissions for performing the functions of each user -the principle of least privilege.
Defines a single point of control for network access. From this centralized point administrators can deploy access policies and other key aspects for network security orchestration, for take reactive and proactive actions.
Double authentication factor using (OTP) -for user’s identity validation in remote connections.
Shows the real-time statistics and authentication details in the network, using dashboards to monitor the authentication processes of users and devices.
Facilitates the adaptation of standards and frameworks such as ISO2700x, NIST, ENS etc.
4.2.1.3. UNAC in 4 Steps
The UNAC configuration and operation process involve the following 4 steps:
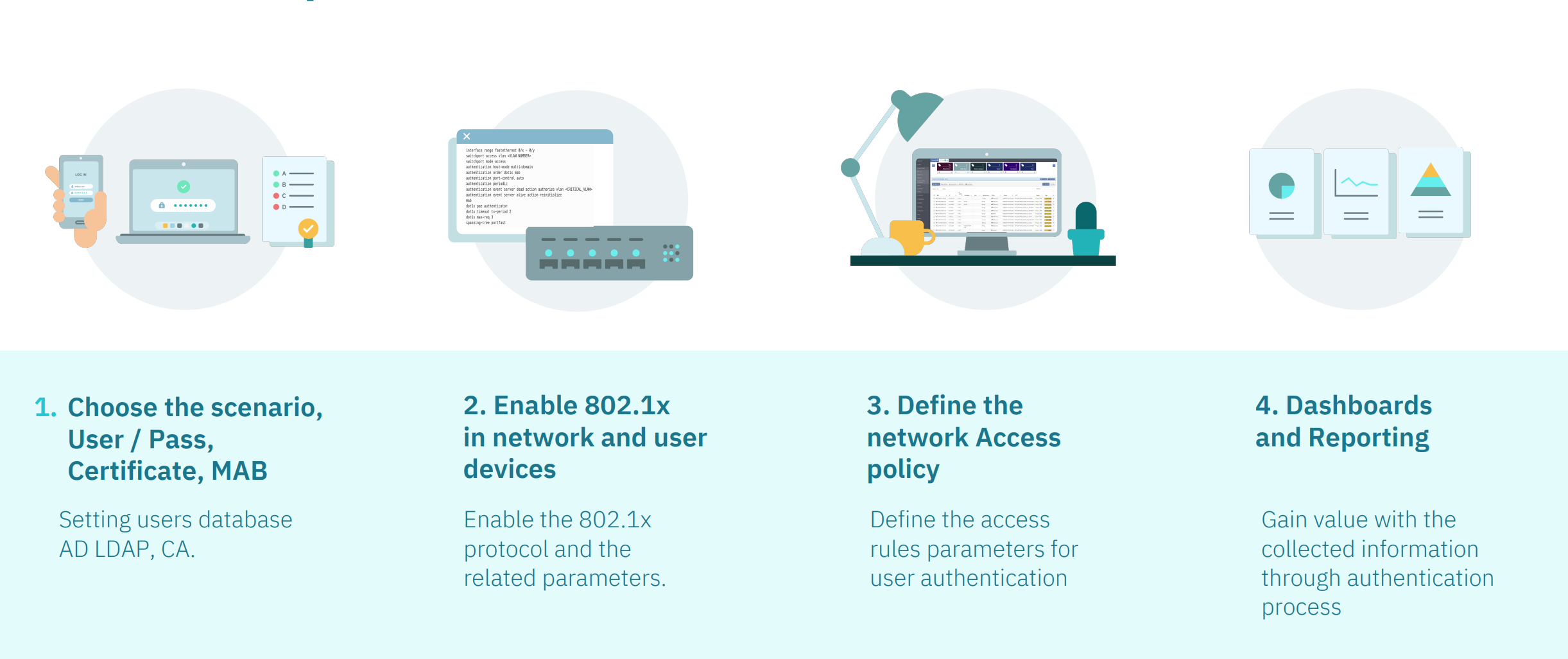
The first two steps are explained in the Configuration documentation and the last two are in the UNAC operation.
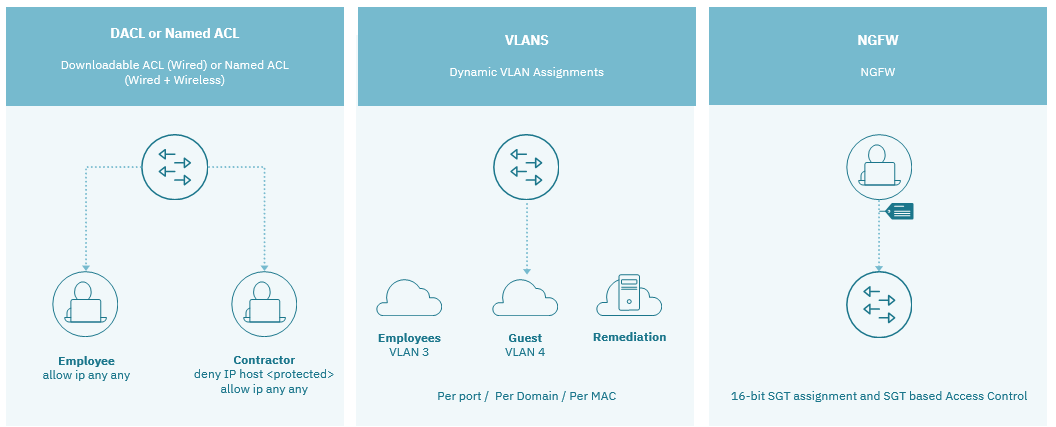
4.2.1.4. Authentication Scenarios
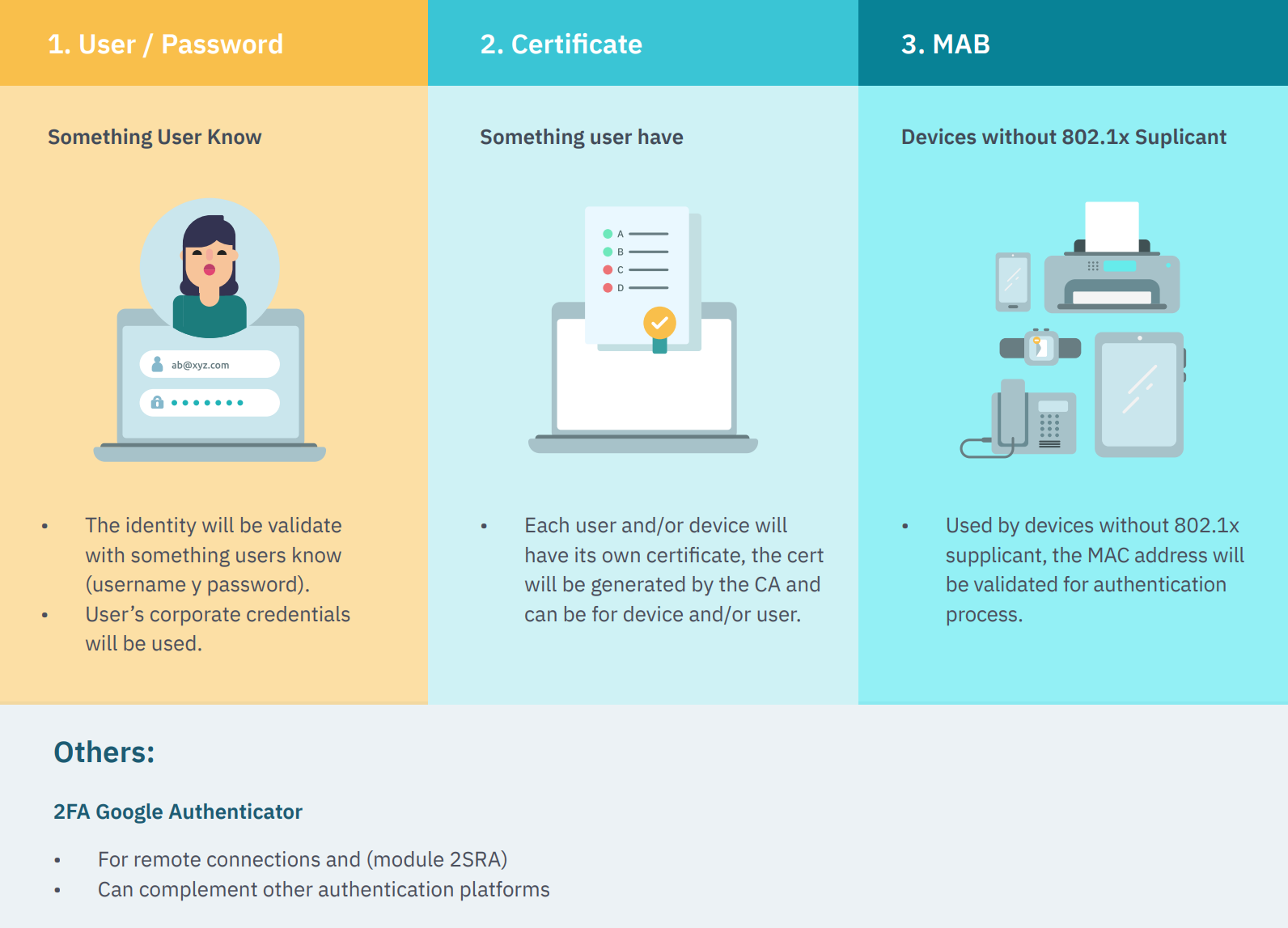
- User and Pass
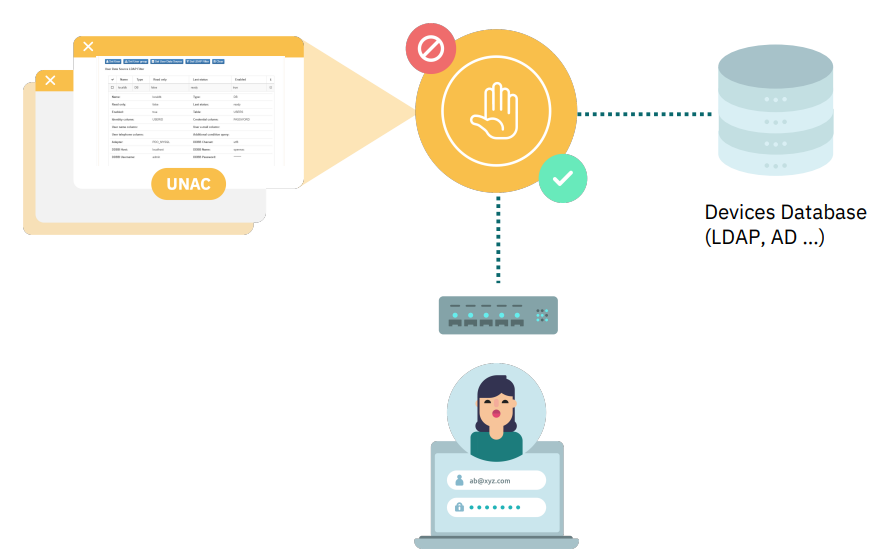
The identity will be validated with something users know (username y password).
User’s corporate credentials will be used.
- Certificate
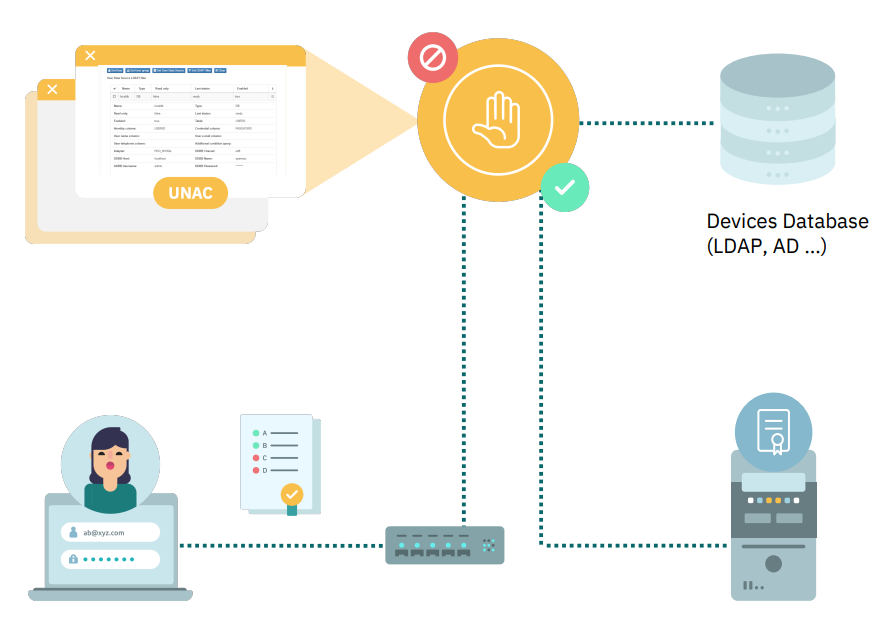
Each user and/or device will have its own certificate. The certificate will be generated by the CA and can be for a device and/or user.
- MAB
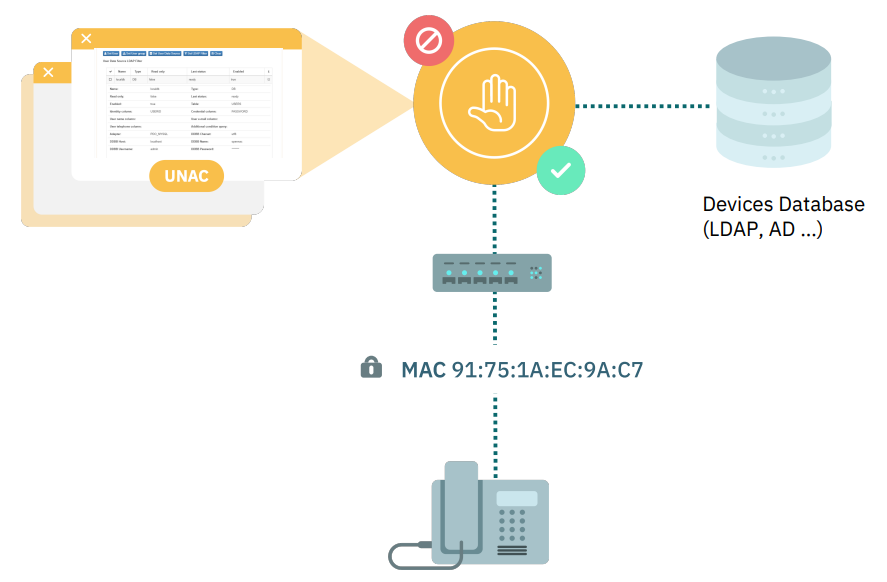
Used by devices without 802.1x supplicant, the MAC address will be validated for authentication process.
- Others:
- 2FA Google Authenticator
Remote connections and 2SRA module
Complement other authentication platforms
4.2.1.4.1. User and Pass
|
|
4.2.1.4.2. Certificate
|
|
4.2.1.4.3. MAB
|
|
4.2.1.6. UNAC Value
4.2.1.6.1. IT Support/ Help Desk
Reducing incidents response time: identify the affected device from the CMDB (username, IP, MAC, etc.) and toggle the related port on the switch (Toggle Port).
4.2.1.6.2. Monitoring - IT management
Real-time connections information Control Dashboards.
- Users’ connection metrics:
Wi-Fi users
Wired users
User’s information (location)
User’s rol
- Devices Information:
Device topology
Device location
Device information
MAC
Vendor
4.2.1.6.3. Adaptability
The value is subjective. The perception of the value of an IT tool increases as they solve a given problem.
The adaptability degree of IT tools will determine the value they provide.
UNAC module integrates with the current company’s infrastructure. It does not add administration efforts, but rather automates some recurring tasks, removing some mechanical tasks from the technical team.
Eliminate technological rigidity
Task automation
Multi-vendor, agnostic technology
Plugins, integrations
4.2.1.6.4. Dashboards Customization

The administrator selects the visualization type to set the Dashboard graphics(Bars, cake, etc).
Select the information, the device data (TAGS) that you want to show from the CMDB.
Set the structure of dashboards and selects all visualization.
Generate a new dashboard adding all the visualizations you want.
Add the dashboard to the OpenNAC Enterprise web console.
4.2.1.6.5. Reports. Audit Teams.
Management and audit reports in real-time:
Dashboards with users authentication details are automatically updated in real-time.
Companies can choose how to segment authenticated users on the network to have a report available at any time.
Examples:
Authenticated users
Authentication sources
Connected users from a certain group.
Users location